linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py¶
Description
The linear elastodynamics solution of an iron plate impact problem with identification of material parameters from simulated measurement data.
Find 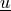 such that:
such that:
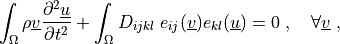
where
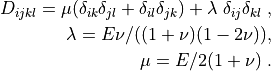
Usage Examples¶
Run without the identification:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py sfepy-view output/edi/user_block.h5 -f u:wu:f1e3:p0 1:vw:p0
Get help:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py -h
Run the identification with default parameters, show live plot of convergence and launch ipython shell after the computation:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --plot-log --shell
Result figures are in output/edi, if not changed using –output-dir option.
Check the Jacobian matrix by finite differences:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --opt-conf=max_nfev=1 --check-jac --shell
Identify also the damping parameters (zero by default):
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --par-names=young,poisson,density,alpha,beta --plot-log --shell
See also linear_elasticity/elastodynamic.py.
r"""
The linear elastodynamics solution of an iron plate impact problem with
identification of material parameters from simulated measurement data.
Find :math:`\ul{u}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \rho \ul{v} \pddiff{\ul{u}}{t}
+ \int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl} \;,
\lambda = E \nu / ((1 + \nu)(1 - 2\nu)), \\ \mu = E / 2(1 + \nu)
\;.
Usage Examples
--------------
- Run without the identification::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py
sfepy-view output/edi/user_block.h5 -f u:wu:f1e3:p0 1:vw:p0
- Get help::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py -h
- Run the identification with default parameters, show live plot of
convergence and launch ipython shell after the computation::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --plot-log --shell
Result figures are in output/edi, if not changed using --output-dir option.
- Check the Jacobian matrix by finite differences::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --opt-conf=max_nfev=1 --check-jac --shell
- Identify also the damping parameters (zero by default)::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/elastodynamic_identification.py --par-names=young,poisson,density,alpha,beta --plot-log --shell
See also :ref:`linear_elasticity-elastodynamic`.
"""
from argparse import ArgumentParser, RawDescriptionHelpFormatter
import sys
import os.path as op
from functools import partial
import numpy as nm
import scipy.sparse as sps
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sfepy.base.base import output, Struct, IndexedStruct
from sfepy.base.conf import dict_from_string as parse_as_dict
from sfepy.discrete.fem.meshio import UserMeshIO
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
from sfepy.homogenization.utils import define_box_regions
from sfepy.solvers import register_solver, Solver
from sfepy.base.timing import Timer
import sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs as mc
def define(
young=200e9, poisson=0.3, density=7800,
alpha=0.0, beta=0.0,
plane='strain',
dims=(1e-2, 2.5e-3, 2.5e-3),
shape=(21, 6, 6),
v0=1.0,
ct1=1.5,
dt=None,
active_only=False,
save_times=20,
output_dir='output/edi',
**kwargs,
):
"""
Parameters
----------
young, poisson, density: material parameters
plane: plane strain or stress hypothesis
dims: physical dimensions of the block (L, d, x)
shape: numbers of mesh vertices along each axis
v0: initial impact velocity
ct1: final time in L / "longitudinal wave speed" units
dt: time step (None means automatic)
save_times: number of time steps to save
output_dir: output directory
"""
dim = len(dims)
lam, mu = mc.lame_from_youngpoisson(young, poisson, plane=plane)
# Longitudinal and shear wave propagation speeds.
cl = nm.sqrt((lam + 2.0 * mu) / density)
cs = nm.sqrt(mu / density)
# Element size.
L, d = dims[:2]
H = L / (nm.max(shape) - 1)
# Time-stepping parameters.
if dt is None:
# For implicit schemes, dt based on the Courant number C0 = dt * cl / H
# equal to 1.
dt = H / cl # C0 = 1
t1 = ct1 * L / cl
def mesh_hook(mesh, mode):
"""
Generate the block mesh.
"""
if mode == 'read':
mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, 0.5 * nm.array(dims),
name='user_block', verbose=False)
return mesh
elif mode == 'write':
pass
filename_mesh = UserMeshIO(mesh_hook)
bbox = [[0] * dim, dims]
regions = define_box_regions(dim, bbox[0], bbox[1], 1e-5)
dx = dims[0] / (shape[0] - 1)
sx = int(0.2 * (shape[0] - 1)) * dx
regions.update({
'Omega' : 'all',
'Plane' : ('vertices in (x > %.12f) & (x < %.12f)'
% (0.99999 * sx, 1.00001 * sx),
'facet'),
})
if dim == 3:
regions.update({
'Sensor' : ('r.Plane *v r.Top *v r.Far', 'vertex'),
})
else:
regions.update({
'Sensor' : ('r.Plane *v r.Top', 'vertex'),
})
# Iron.
materials = {
'm' : ({
'young' : young,
'poisson' : poisson,
'density': density,
},),
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2,
}
# Notes:
# 1. The order of the variables in the solution vector is specified here
# (3rd tuple member), since that specific order is expected by the
# elastodynamic time-stepping solvers.
# 2. For the same reason, we won't explicitly define below the equations
# du = du/dt and ddu = ddu/dt - these are implicitly defined by
# the time-stepping solver. see the `step()` method of the solvers.
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'du' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 1),
'ddu' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 2),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
'dv' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'du'),
'ddv' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'ddu'),
}
# The mapping of variables for the elastodynamics solvers - keys are given,
# values correspond to the names of the actual variables.
var_names = {'u' : 'u', 'du' : 'du', 'ddu' : 'ddu'}
ebcs = {
'Impact' : ('Left', {'u.0' : 0.0, 'du.0' : 0.0, 'ddu.0' : 0.0}),
}
if dim == 3:
ebcs.update({
'Symmtery-y' : ('Near',
{'u.1' : 0.0, 'du.1' : 0.0, 'ddu.1' : 0.0}),
'Symmetry-z' : ('Bottom',
{'u.2' : 0.0, 'du.2' : 0.0, 'ddu.2' : 0.0}),
})
def get_ic(coor, ic, mode='u'):
val = nm.zeros_like(coor)
if mode == 'u':
val[:, 0] = 0.0
elif mode == 'du':
val[:, 0] = -1.0
return val
functions = {
'get_ic_u' : (get_ic,),
'get_ic_du' : (lambda coor, ic: get_ic(coor, None, mode='du'),),
}
ics = {
'ic' : ('Omega', {'u.all' : 'get_ic_u', 'du.all' : 'get_ic_du'}),
}
equations = {
'eq' :
f"""
+ dw_mass_ad.i.Omega(m.density, ddv, ddu)
+ {alpha} * dw_mass_ad.i.Omega(m.density, dv, du)
+ {beta} * dw_lin_elastic_yp_ad.i.Omega(m.young, m.poisson, dv, du)
+ dw_lin_elastic_yp_ad.i.Omega(m.young, m.poisson, v, u) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'lsd' : ('ls.auto_direct', {
# 'lsd' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {
# Reuse the factorized linear system from the first time step.
'use_presolve' : True,
# Speed up the above by omitting the matrix digest check used
# normally for verification that the current matrix corresponds to
# the factorized matrix stored in the solver instance. Use with
# care!
'use_mtx_digest' : False,
# Increase when getting MUMPS error -9.
'memory_relaxation' : 50,
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-6,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
}),
'tsn' : ('ts.newmark', {
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'beta' : 0.25,
'gamma' : 0.5,
'var_names' : var_names,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
}
options = {
'ts' : 'tsn',
'tsc' : None,
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'lsd',
'save_times' : save_times,
'active_only' : active_only,
'auto_transform_equations' : False,
'output_format' : 'h5',
'output_dir' : output_dir,
}
return locals()
from sfepy.solvers.ts_solvers import NewmarkTS, _cache
class NewmarkSATS(NewmarkTS):
r"""
Solve elastodynamics problems by the Newmark method.
The method was introduced in [1]. Common settings [2]:
==================== ======== ==== ===== ==========
name kind beta gamma Omega_crit
==================== ======== ==== ===== ==========
trapezoidal rule: implicit 1/4 1/2 unconditional
linear acceleration: implicit 1/6 1/2 :math:`2\sqrt{3}`
Fox-Goodwin: implicit 1/12 1/2 :math:`\sqrt{6}`
central difference: explicit 0 1/2 2
==================== ======== ==== ===== ==========
All of these methods are 2-order of accuracy.
[1] Newmark, N. M. (1959) A method of computation for structural dynamics.
Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE, 85 (EM3) 67-94.
[2] Arnaud Delaplace, David Ryckelynck: Solvers for Computational Mechanics
"""
name = 'ts.newmark_sa'
def create_nlst(self, nls, dt, gamma, beta, u0, e0, v0, a0, pack, unpack):
dt2 = dt**2
iue, iu, ie, iv, ia = pack.indices
if iue != iu:
raise ValueError('extra variables not supported!')
cc0 = (1.0 - gamma) * dt
cc = gamma * dt
ck0 = (0.5 - beta) * dt2
ck = beta * dt2
def v(a):
return v0 + cc0 * a0 + cc * a
def u(a):
return u0 + dt * v0 + ck0 * a0 + ck * a
def fun(at):
vec = nm.r_[u(at), v(at), at]
aux = nls.fun(vec)
rt = aux[iu] + aux[iv] + aux[ia]
return rt
@_cache(self, 'matrix', self.conf.is_linear)
def fun_grad(at):
vec = None if self.conf.is_linear else nm.r_[u(at), v(at), at]
M, C, K = self.get_matrices(nls, vec, unpack)
Kt = M + cc * C + ck * K
return Kt
@_cache(self, 'matrix_sa', self.conf.is_linear and (self.ts.step > 0))
def efun_grad(at):
vec = None if self.conf.is_linear else nm.r_[u(at), v(at), at]
M, C, K = self.get_matrices(nls, vec, unpack)
size = at.shape[0]
I = sps.eye(size, dtype=nm.float64)
zz = sps.dia_matrix((size, size), dtype=nm.float64)
if self.ts.step > 0:
duda = -ck * I
dvda = -cc * I
else:
duda = dvda = zz
# The initial state might depend on parameters - it does not in
# this example as u0 = 0, v0 = const and a0 = 0, but the
# following code should work in the general case if the next
# line is commented out.
K = C = zz
return sps.bmat([[K, C, M],
[I, zz, duda],
[zz, I, dvda]])
@_cache(self, 'matrix_sa0', self.conf.is_linear and (self.ts.step > 0))
def efun_grad0(at):
if self.ts.step > 0:
size = at.shape[0]
I = sps.eye(size, dtype=nm.float64)
zz = sps.dia_matrix((size, size), dtype=nm.float64)
duda0 = -ck0 * I
dudv0 = -dt * I
dudu0 = -I
dvda0 = -cc0 * I
dvdv0 = -I
return sps.bmat([[zz, zz, zz],
[dudu0, dudv0, duda0],
[zz, dvdv0, dvda0]])
else:
return sps.csr_matrix((self.sa_info.n_dof, self.sa_info.n_dof),
dtype=nm.float64)
def efun_grad_par(at):
mtx = nm.zeros((self.sa_info.n_dof, self.sa_info.n_par),
dtype=nm.float64, order='F')
mtx = self.context.equations.evaluate(
mode='weak', dw_mode='sensitivity',
diff_vars=self.sa_info.par_names, asm_obj=mtx,
)
for ic, name in enumerate(self.sa_info.par_names):
if name == 'alpha': # = M v
info = self.sa_info.par_info['alpha']
elif name == 'beta': # = K v
info = self.sa_info.par_info['beta']
else:
continue
term = self.context.equations[info[1]].terms[info[2]]
val, iels, status = term.evaluate(mode='weak',
diff_var=None,
standalone=False,
ret_status=True)
val /= term.sign
term.assemble_to(mtx[:, ic], val, iels)
Vt = mtx[iu] + mtx[iv] + mtx[ia]
zz = nm.zeros_like(Vt, dtype=nm.float64)
return nm.block([[Vt],
[zz],
[zz]])
nlst = nls.copy()
nlst.fun = fun
nlst.fun_grad = fun_grad
nlst.efun_grad = efun_grad
nlst.efun_grad0 = efun_grad0
nlst.efun_grad_par = efun_grad_par
nlst.u = u
nlst.v = v
self.nlst = nlst
return nlst
register_solver(NewmarkSATS)
def apply_sensor(pb, ts, state, out):
us = state['u'].get_state_in_region(pb.domain.regions['Sensor'])
output('sensor', ts.step, us)
out.append(us)
def update_pars(materials, equations, pars, par_names, par_info):
"""
Materials and options are updated in place.
"""
done = set()
for key in par_names:
if key in done: continue
info = par_info[key]
ip = par_names.index(key)
if info[0] == 'term': # Update term coefficient.
equations[info[1]].terms[info[2]].sign = pars[ip]
else: # Update materials.
mat = materials[info[0]]
mkeys = mat.get_keys(info[1])
for mkey in mkeys:
if key == info[2]:
val = pars[ip]
else:
raise ValueError
mat.datas[mkey][info[2]][:, :] = val
output('updated:', par_names)
def eval_fun(pars, data, pb, options, par_names, par_info, opt_data, plog,
inodir):
opt_data.tfun.start()
materials = pb.get_materials()
update_pars(materials, pb.equations, pars, par_names, par_info)
pb.ts.set_step() # Reset ts.
pb.get_solver().clear_lin_solver() # No digest -> clear manually.
out = []
pb.solve(save_results=False, step_hook=partial(apply_sensor, out=out))
usens = nm.concatenate(out)
sim_data = usens[:, -1]
res = sim_data - data
plog(*(tuple(pars) + (nm.linalg.norm(res),)))
times = pb.ts.times
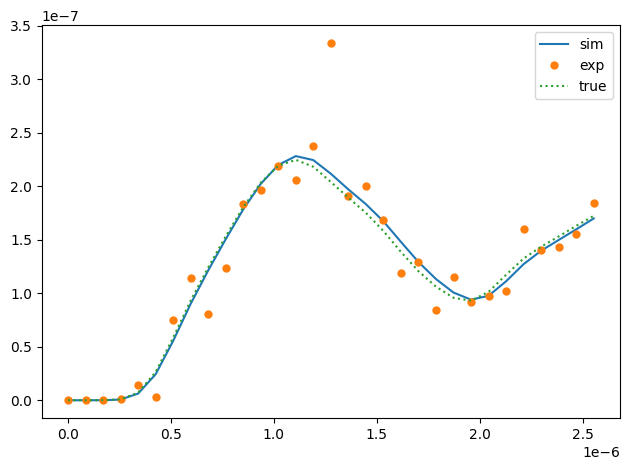
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(times, sim_data, label='sim')
ax.plot(times, data, ls='', marker='o', mew=0, label='exp')
ax.plot(times, opt_data.true_data, ls=':', label='true')
ax.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
fig.savefig(inodir(f'res{opt_data.n_fun:05d}.png'), bbox_inches='tight')
opt_data.n_fun += 1
opt_data.usens = usens
dt = opt_data.tfun.stop()
output(f'function evaluation done in {dt} s.')
return res
def eval_jac_fd(pars, *args, **kwargs):
v0 = eval_fun(pars, *args, **kwargs)
eps = 1e-6
jac = []
for ip, par in enumerate(pars):
pars1 = pars.copy()
dp = eps * par
pars1[ip] += dp
v1 = eval_fun(pars1, *args, **kwargs)
jac.append((v1 - v0) / dp)
jac = nm.array(jac).T
return jac
def eval_jac(pars, data, pb, options, par_names, par_info, opt_data, plog,
inodir):
opt_data.tjac.start()
materials = pb.get_materials()
update_pars(materials, pb.equations, pars, par_names, par_info)
pb.ts.set_step() # Reset ts.
pb.get_solver().clear_lin_solver() # No digest -> clear manually.
variables = pb.get_initial_state()
n_dof = variables.adi.n_dof_total
n_par = len(par_names)
_tss = pb.get_solver()
conf = _tss.conf.copy(name='tss_sa')
conf.kind = 'ts.newmark_sa'
tss = Solver.any_from_conf(conf, nls=_tss.nls, tsc=_tss.tsc, context=pb)
tss.sa_info = Struct(
par_info=par_info, par_names=par_names, n_par=n_par, n_dof=n_dof,
)
tss.matrix_sa = tss.matrix_sa0 = tss.matrix_pars = None
ls = Solver.any_from_conf(tss.nls.lin_solver.conf)
_init_fun, prestep_fun, _poststep_fun = pb.get_tss_functions(
update_bcs=True, update_materials=True,
save_results=False,
step_hook=None, post_process_hook=None,
)
fu = pb.fields['displacement']
ii = fu.get_dofs_in_region(pb.domain.regions['Sensor'])[0]
idof = int(fu.n_components * ii + 2 + variables.adi.indx['u'].start)
def init_fun(tss, ts, vec0):
vec0 = _init_fun(ts, vec0)
# Previous step dy/da.
tss.gy0 = nm.zeros((tss.sa_info.n_dof, tss.sa_info.n_par),
dtype=nm.float64, order='F')
return vec0
jac = []
def poststep_fun(tss, ts, vec):
# EBCs need to be applied here because of algebraically computed
# variables in elastodynamics solvers.
variables.set_state(vec, pb.active_only, apply_ebc=True)
unpack = tss.unpack
utp, etp, vtp, atp = unpack(vec)
if ts.step == 0:
nlst = tss.create_nlst(tss.nls, ts.dt, tss.conf.gamma, tss.conf.beta,
utp, etp, vtp, atp, tss.pack, unpack)
else:
nlst = tss.nlst
Atp = nlst.efun_grad(atp)
Wtp = nlst.efun_grad0(atp)
Vtp = nlst.efun_grad_par(atp)
ry = -(Vtp + Wtp @ tss.gy0)
if options.multi_rhs:
gy = ls(ry, mtx=Atp)
else:
gy = nm.empty_like(ry)
for ic in range(gy.shape[1]):
gy[:, ic] = ls(ry[:, ic], mtx=Atp)
if ts.step == 0:
# No digest -> clear manually.
ls.clear()
jac.append(gy[idof])
tss.gy0 = gy
pb.advance(ts)
return vec
tss.set_dof_info(variables.adi)
status = IndexedStruct()
tss(variables.get_state(pb.active_only, force=True),
init_fun=init_fun,
prestep_fun=prestep_fun,
poststep_fun=poststep_fun,
status=status)
jac = nm.array(jac)
if options.check_jac:
jac_fd = eval_jac_fd(pars, data, pb, options, par_names, par_info,
opt_data, plog, inodir)
output('Jacobian:')
output(jac)
output('Jacobian using finite differences:')
output(jac_fd)
output('Relative difference:')
output((jac_fd - jac) / nm.where(jac_fd, jac_fd, 1.0))
opt_data.jac = jac.copy()
opt_data.jac_fd = jac_fd
opt_data.n_jac += 1
dt = opt_data.tjac.stop()
output(f'jacobian evaluation done in {dt} s.')
return jac
def parse_args(args=None):
helps = {}
sdefault_opt_conf = """ftol=1e-08, xtol=1e-4, gtol=None, method='trf',
f_scale=3e-8, loss='soft_l1', verbose=2
"""
opts = dict(
par_names = ('density,young,poisson', 'parameters to be identified'),
opt_conf = (sdefault_opt_conf, 'optimization solver options'),
jac = (True, 'do not use the semi-analytical Jacobian calculation'),
check_jac = (False,
'check the Jacobian using finite differences'),
multi_rhs = (False, 'solve all rhs of sensitivity analysis in one call'),
young = (200e9, """Young's modulus"""),
poisson = (0.3, """Poisson's ratio"""),
density = (7800.0, 'density'),
alpha = (0.0, 'proportional damping coefficient (M)'),
beta = (0.0, 'proportional damping coefficient (K)'),
dims = ('1e-2,2.5e-3,2.5e-3',
'physical dimensions of the block (L, d, x)'),
shape = ('21,6,6',
'numbers of mesh vertices along each axis'),
v0 = (1.0, 'initial impact velocity'),
ct1 = (1.5, 'final time in L / "longitudinal wave speed" units'),
dt = (None, 'time step (None means automatic)'),
active_only = (False,
'vectors and matrices contain only active DOFs'),
save_times = (20, 'number of time steps to save'),
output_dir = ('output/edi', 'output directory'),
plot_log = (False, 'show live log figures'),
shell = (False, 'run ipython shell after all computations'),
debug = (False,
'automatically start debugger when an exception is raised'),
)
parser = ArgumentParser(description=__doc__.rstrip(),
formatter_class=RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
dhelp = ' [default: %(default)s]'
for key, (val, msg) in opts.items():
helps[key] = msg
action = 'store'
vtype = type(val)
choices = None
option = key
if val is True:
action = 'store_false'
option = 'no_' + key
elif val is False:
action = 'store_true'
elif isinstance(val, tuple):
choices = val
vtype = type(val[0])
val = val[0]
elif isinstance(val, list):
vtype = type(val[1])
val = val[0]
if action == 'store':
helps[key] += dhelp
parser.add_argument('--' + option.replace('_', '-'),
type=vtype,
action=action, dest=key, choices=choices,
default=val, help=helps[key])
else:
parser.add_argument('--' + option.replace('_', '-'),
action=action, dest=key,
default=val, help=helps[key])
options = parser.parse_args(args=args)
options.dims = [float(ii) for ii in options.dims.split(',')]
options.shape = [int(ii) for ii in options.shape.split(',')]
options.par_names = [ii.strip() for ii in options.par_names.split(',')]
aux = parse_as_dict(sdefault_opt_conf)
aux.update(parse_as_dict(options.opt_conf))
options.opt_conf = aux
options.plane = 'strain'
options.opt_bounds = {
'density' : [0.5 * options.density, 1.5 * options.density],
'young' : [0.5 * options.young, 1.5 * options.young],
'poisson' : [0.9 * options.poisson, 1.1 * options.poisson],
'alpha' : [0, 1e4],
'beta' : [0, 1e-4],
}
return options, helps
def main():
from scipy.optimize import least_squares
from sfepy.base.base import output, Struct
from sfepy.base.conf import ProblemConf
from sfepy.discrete import Problem
from sfepy.base.log import Log
options, helps = parse_args()
if options.debug:
from sfepy.base.base import debug_on_error; debug_on_error()
conf = ProblemConf.from_dict(define(**vars(options)), sys.modules[__name__])
pb = Problem.from_conf(conf)
out = []
pb.solve(save_results=False, step_hook=partial(apply_sensor, out=out))
usens = nm.concatenate(out)
size = nm.abs(usens[:, -1]).max()
true_data = usens[:, -1]
data = true_data.copy()
i0 = int(0.2 * options.shape[0])
data[i0:] += nm.random.default_rng(seed=42).normal(
0, 0.1 * size, len(data[i0:]),
)
# Add an outlier.
data[max(len(data) // 2, i0)] += 0.5 * size
par_info = {
'density' : ('m', 'Omega', 'density', options.density),
'young' : ('m', 'Omega', 'young', options.young * 0.8),
'poisson' : ('m', 'Omega', 'poisson', options.poisson),
'alpha' : ('term', 'eq', 1, 1000),
'beta' : ('term', 'eq', 2, 1e-5),
}
par_names = options.par_names
all_par_names = set(par_info.keys())
if not set(par_names).issubset(all_par_names):
unknown = set(par_names).difference(all_par_names)
raise ValueError(f'parameters {unknown} not in {all_par_names}!')
labels = [[name] for name in par_names] + [['|res|']]
nlog = len(labels)
formats = [['{:.16e}' for ii in range(len(labs))] for labs in labels]
inodir = partial(op.join, options.output_dir)
plog = Log(labels,
formats=formats,
yscales=['log'] * nlog,
xlabels=['iter'] * nlog,
ylabels=None,
show_legends=True,
is_plot=options.plot_log,
log_filename=inodir('pars.txt'),
aggregate=1000, sleep=0.1)
pars0 = [par_info[name][-1] for name in par_names]
pars0 = nm.array(pars0, dtype=nm.float64)
x_scale = [par if abs(par) > 0 else 1.0 for par in pars0]
bounds = [options.opt_bounds.get(name, (-nm.inf, nm.inf))
for name in par_names]
bounds = tuple(zip(*bounds))
opt_data = Struct(name='opt_data', true_data=true_data, n_fun=0, n_jac=0,
tfun=Timer('fun'), tjac=Timer('jac'))
timer = Timer(start=True)
res = least_squares(
eval_fun, pars0,
jac=eval_jac if options.jac else '2-point',
bounds=bounds,
x_scale=x_scale,
args=(data, pb, options, par_names, par_info, opt_data, plog, inodir),
**options.opt_conf
)
elapsed = timer.stop()
output(f'identification done in {elapsed} s.')
output(res)
od = opt_data
tfi = od.tfun.total / od.n_fun
tji = od.tjac.total / max(od.n_jac, 1)
tfe = tfi * len(pars0)
output(f'evaluations: function: {od.n_fun}, jacobian: {od.n_jac}')
output(f'elapsed: function: {od.tfun.total}, jacobian {od.tjac.total}')
output(f'elapsed/it: function: {tfi}, jacobian {tji}')
output(f'expected finite difference jacobian time: {tfe}')
plog(save_figure=inodir('pars.png'))
if options.shell:
from sfepy.base.base import shell; shell()
plog(finished=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()