diffusion/poisson_field_dependent_material.py¶
Description
Laplace equation with a field-dependent material parameter.
Find 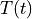 for
for ![t \in [0, t_{\rm final}]](../_images/math/9f80775f131863202ea25954249a43c09294920c.png) such that:
such that:
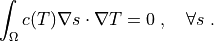
where 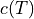 is the
is the 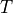 dependent diffusion coefficient.
Each iteration calculates
dependent diffusion coefficient.
Each iteration calculates 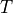 and adjusts
and adjusts 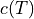 .
.
r"""
Laplace equation with a field-dependent material parameter.
Find :math:`T(t)` for :math:`t \in [0, t_{\rm final}]` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} c(T) \nabla s \cdot \nabla T
= 0
\;, \quad \forall s \;.
where :math:`c(T)` is the :math:`T` dependent diffusion coefficient.
Each iteration calculates :math:`T` and adjusts :math:`c(T)`.
"""
from sfepy import data_dir
from sfepy.base.base import output
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/cylinder.mesh'
t0 = 0.0
t1 = 0.1
n_step = 11
def get_conductivity(ts, coors, problem, equations=None, mode=None, **kwargs):
"""
Calculates the conductivity as 2+10*T and returns it.
This relation results in larger T gradients where T is small.
"""
if mode == 'qp':
# T-field values in quadrature points coordinates given by integral i
# - they are the same as in `coors` argument.
T_values = problem.evaluate('ev_integrate.i.Omega(T)',
mode='qp', verbose=False)
val = 2 + 10 * (T_values + 2)
output('conductivity: min:', val.min(), 'max:', val.max())
val.shape = (val.shape[0] * val.shape[1], 1, 1)
return {'val' : val}
materials = {
'coef' : 'get_conductivity',
}
fields = {
'temperature' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'T' : ('unknown field', 'temperature', 0),
's' : ('test field', 'temperature', 'T'),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Gamma_Left' : ('vertices in (x < 0.00001)', 'facet'),
'Gamma_Right' : ('vertices in (x > 0.099999)', 'facet'),
}
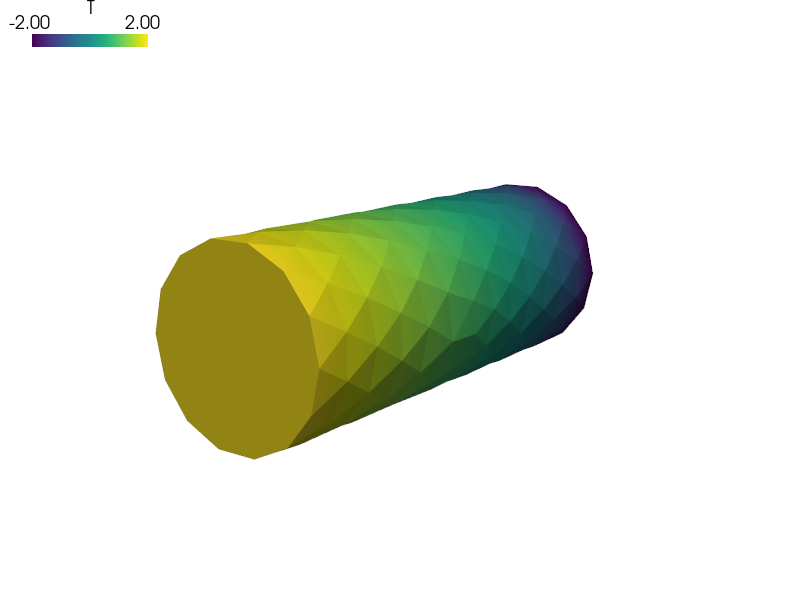
ebcs = {
'T1' : ('Gamma_Left', {'T.0' : 2.0}),
'T2' : ('Gamma_Right', {'T.0' : -2.0}),
}
functions = {
'get_conductivity' : (get_conductivity,),
}
ics = {
'ic' : ('Omega', {'T.0' : 0.0}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 1,
}
equations = {
'Temperature' : """dw_laplace.i.Omega( coef.val, s, T ) = 0"""
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
}),
'ts' : ('ts.simple', {
't0' : t0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : None,
'n_step' : n_step, # has precedence over dt!
'quasistatic' : True,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
}
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
'ts' : 'ts',
'save_times' : 'all',
}