diffusion/poisson_functions.py¶
Description
Poisson equation with source term.
Find 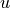 such that:
such that:
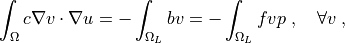
where 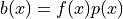 ,
, 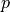 is a given FE field and
is a given FE field and 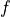 is
a given general function of space.
is
a given general function of space.
This example demonstrates use of functions for defining material parameters, regions, parameter variables or boundary conditions. Notably, it demonstrates the following:
How to define a material parameter by an arbitrary function - see the function
get_pars()that evaluates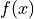 in quadrature
points.
in quadrature
points.How to define a known function that belongs to a given FE space (field) - this function,
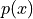 , is defined in a FE sense by its nodal values
only - see the function
, is defined in a FE sense by its nodal values
only - see the function get_load_variable().
In order to define the load 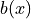 directly, the term
directly, the term dw_dot
should be replaced by dw_integrate.
r"""
Poisson equation with source term.
Find :math:`u` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} c \nabla v \cdot \nabla u
= - \int_{\Omega_L} b v = - \int_{\Omega_L} f v p
\;, \quad \forall v \;,
where :math:`b(x) = f(x) p(x)`, :math:`p` is a given FE field and :math:`f` is
a given general function of space.
This example demonstrates use of functions for defining material parameters,
regions, parameter variables or boundary conditions. Notably, it demonstrates
the following:
1. How to define a material parameter by an arbitrary function - see the
function :func:`get_pars()` that evaluates :math:`f(x)` in quadrature
points.
2. How to define a known function that belongs to a given FE space (field) -
this function, :math:`p(x)`, is defined in a FE sense by its nodal values
only - see the function :func:`get_load_variable()`.
In order to define the load :math:`b(x)` directly, the term ``dw_dot``
should be replaced by ``dw_integrate``.
"""
import numpy as nm
from sfepy import data_dir
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/cylinder.mesh'
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
}
materials = {
'm' : ({'c' : 1.0},),
'load' : 'get_pars',
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Omega_L' : 'vertices by get_middle_ball',
'Gamma_Left' : ('vertices in (x < 0.00001)', 'facet'),
'Gamma_Right' : ('vertices in (x > 0.099999)', 'facet'),
}
fields = {
'temperature' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
'velocity' : ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'temperature', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'temperature', 'u'),
'p' : ('parameter field', 'temperature',
{'setter' : 'get_load_variable'}),
'w' : ('parameter field', 'velocity',
{'setter' : 'get_convective_velocity'}),
}
ebcs = {
'u1' : ('Gamma_Left', {'u.0' : 'get_ebc'}),
'u2' : ('Gamma_Right', {'u.0' : -2.0}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 1,
}
equations = {
'Laplace equation' :
"""dw_laplace.i.Omega( m.c, v, u )
- dw_convect_v_grad_s.i.Omega( v, w, u )
= - dw_dot.i.Omega_L( load.f, v, p )"""
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
}),
}
def get_pars(ts, coors, mode=None, **kwargs):
"""
Evaluate the coefficient `load.f` in quadrature points `coors` using a
function of space.
For scalar parameters, the shape has to be set to `(coors.shape[0], 1, 1)`.
"""
if mode == 'qp':
x = coors[:, 0]
val = 55.0 * (x - 0.05)
val.shape = (coors.shape[0], 1, 1)
return {'f' : val}
def get_middle_ball(coors, domain=None):
r"""
Get the :math:`\Omega_L` region as a function of mesh coordinates.
"""
x, y, z = coors[:, 0], coors[:, 1], coors[:, 2]
r1 = nm.sqrt((x - 0.025)**2.0 + y**2.0 + z**2)
r2 = nm.sqrt((x - 0.075)**2.0 + y**2.0 + z**2)
flag = nm.where((r1 < 2.3e-2) | (r2 < 2.3e-2))[0]
return flag
def get_load_variable(ts, coors, region=None, variable=None, **kwargs):
"""
Define nodal values of 'p' in the nodal coordinates `coors`.
"""
y = coors[:,1]
val = 5e5 * y
return val
def get_convective_velocity(ts, coors, **kwargs):
"""
Define nodal values of 'w' in the nodal coordinates `coors`.
"""
val = 100.0 * nm.ones_like(coors)
return val
def get_ebc(coors, amplitude):
"""
Define the essential boundary conditions as a function of coordinates
`coors` of region nodes.
"""
z = coors[:, 2]
val = amplitude * nm.sin(z * 2.0 * nm.pi)
return val
functions = {
'get_pars' : (get_pars,),
'get_load_variable' : (get_load_variable,),
'get_convective_velocity' : (get_convective_velocity,),
'get_middle_ball' : (get_middle_ball,),
'get_ebc' : (lambda ts, coor, bc, problem, **kwargs: get_ebc(coor, 5.0),),
}