navier_stokes/navier_stokes2d_iga.py¶
Description
Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible fluid flow in 2D solved in a single patch NURBS domain using the isogeometric analysis (IGA) approach.
Find 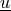 ,
, 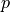 such that:
such that:
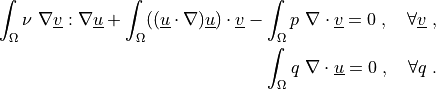
The domain geometry was created by:
sfepy-mesh iga-patch -2 -d 0.1,0.1 -s 10,10 -o meshes/iga/block2d.iga
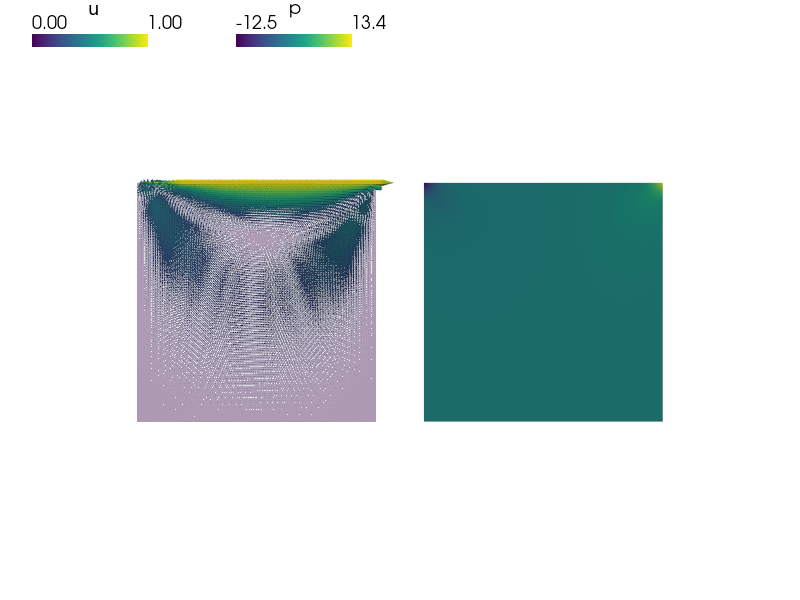
View the results using:
sfepy-view block2d.vtk -2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
r"""
Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible fluid flow in 2D solved in a single
patch NURBS domain using the isogeometric analysis (IGA) approach.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \nu\ \nabla \ul{v} : \nabla \ul{u}
+ \int_{\Omega} ((\ul{u} \cdot \nabla) \ul{u}) \cdot \ul{v}
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;.
The domain geometry was created by::
sfepy-mesh iga-patch -2 -d 0.1,0.1 -s 10,10 -o meshes/iga/block2d.iga
View the results using::
sfepy-view block2d.vtk -2
"""
from sfepy import data_dir
filename_domain = data_dir + '/meshes/iga/block2d.iga'
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Left' : ('vertices of set xi00', 'facet'),
'Right' : ('vertices of set xi01', 'facet'),
'Bottom' : ('vertices of set xi10', 'facet'),
'Top' : ('vertices of set xi11', 'facet'),
'Walls' : ('r.Left +v r.Right +v r.Bottom', 'facet'),
}
materials = {
'fluid' : ({'viscosity' : 1.00e-2},),
}
fields = {
'velocity': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 'iga+1', 'H1', 'iga'),
'pressure': ('real', 'scalar', 'Omega', 'iga', 'H1', 'iga'),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'velocity', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'velocity', 'u'),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure', 1),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
ebcs = {
'1_Walls' : ('Walls', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
'0_Driven' : ('Top', {'u.0' : 1.0, 'u.1' : 0.0}),
'Pressure' : ('Bottom', {'p.0' : 0.0}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 6,
}
equations = {
'balance' :
"""+ dw_div_grad.i.Omega(fluid.viscosity, v, u)
+ dw_convect.i.Omega(v, u)
- dw_stokes.i.Omega(v, p) = 0""",
'incompressibility' :
"""dw_stokes.i.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 15,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
}),
}