navier_stokes/stabilized_navier_stokes.py¶
Description
Stabilized Navier-Stokes problem with grad-div, SUPG and PSPG stabilization solved by a custom Oseen solver.
The stabilization terms are described in [1].
[1] G. Matthies and G. Lube. On streamline-diffusion methods of inf-sup stable discretisations of the generalised Oseen problem. Number 2007-02 in Preprint Series of Institut fuer Numerische und Angewandte Mathematik, Georg-August-Universitaet Goettingen, 2007.
Find 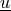 ,
, 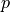 such that:
such that:
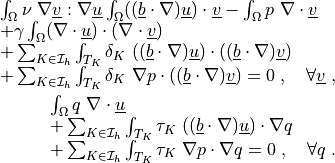
r"""
Stabilized Navier-Stokes problem with grad-div, SUPG and PSPG stabilization
solved by a custom Oseen solver.
The stabilization terms are described in [1].
[1] G. Matthies and G. Lube. On streamline-diffusion methods of inf-sup stable
discretisations of the generalised Oseen problem. Number 2007-02 in Preprint
Series of Institut fuer Numerische und Angewandte Mathematik,
Georg-August-Universitaet Goettingen, 2007.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\begin{array}{l}
\int_{\Omega} \nu\ \nabla \ul{v} : \nabla \ul{u}
\int_{\Omega} ((\ul{b} \cdot \nabla) \ul{u}) \cdot \ul{v}
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v} \\
+ \gamma \int_{\Omega} (\nabla\cdot\ul{u}) \cdot (\nabla\cdot\ul{v}) \\
+ \sum_{K \in \Ical_h}\int_{T_K} \delta_K\ ((\ul{b} \cdot \nabla)
\ul{u})\cdot ((\ul{b} \cdot \nabla) \ul{v}) \\
+ \sum_{K \in \Ical_h}\int_{T_K} \delta_K\ \nabla p\cdot ((\ul{b} \cdot
\nabla) \ul{v})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\end{array}
\begin{array}{l}
\int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u} \\
+ \sum_{K \in \Ical_h}\int_{T_K} \tau_K\ ((\ul{b} \cdot \nabla) \ul{u})
\cdot \nabla q \\
+ \sum_{K \in \Ical_h}\int_{T_K} \tau_K\ \nabla p \cdot \nabla q
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;.
\end{array}
"""
from sfepy.solvers.oseen import StabilizationFunction
from sfepy import data_dir
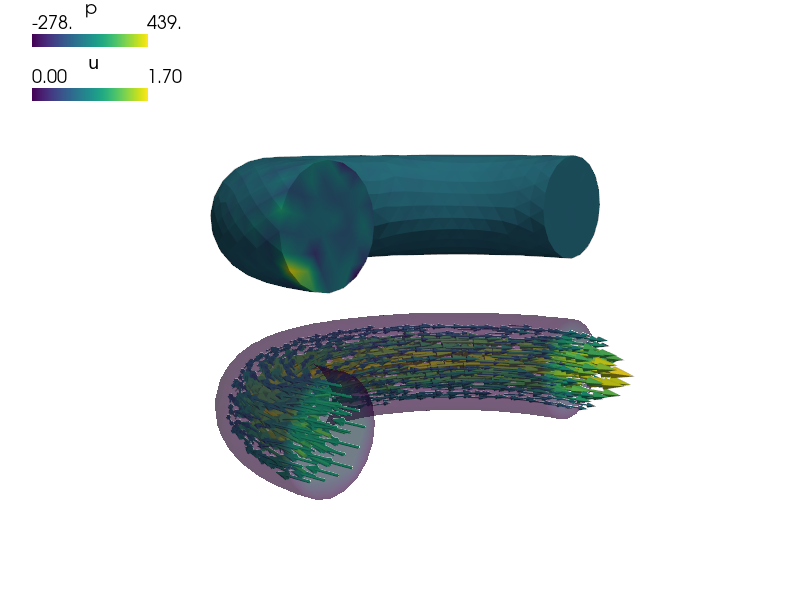
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/elbow2.mesh'
options = {
'solution' : 'steady',
'nls' : 'oseen',
'ls' : 'ls',
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Walls' : ('vertices of surface -v (r.Outlet +v r.Inlet)', 'facet'),
'Inlet' : ('vertices by cinc0', 'facet'),
'Outlet' : ('vertices by cinc1', 'facet'),
}
fields = {
'velocity' : ('real', 3, 'Omega', 1),
'pressure' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'velocity', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'velocity', 'u'),
'b' : ('parameter field', 'velocity', 'u'),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure', 1),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
ebcs = {
'Walls_velocity' : ('Walls', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
'Inlet_velocity' : ('Inlet', {'u.1' : 1.0, 'u.[0,2]' : 0.0}),
}
materials = {
'fluid' : ({'viscosity' : 1.25e-5,
'density' : 1e0},),
'stabil' : 'stabil',
}
integrals = {
'i1' : 2,
'i2' : 3,
}
##
# Stationary Navier-Stokes equations with grad-div, SUPG and PSPG stabilization.
equations = {
'balance' :
""" dw_div_grad.i2.Omega( fluid.viscosity, v, u )
+ dw_lin_convect.i2.Omega( v, b, u )
- dw_stokes.i1.Omega( v, p )
+ dw_st_grad_div.i1.Omega( stabil.gamma, v, u )
+ dw_st_supg_c.i1.Omega( stabil.delta, v, b, u )
+ dw_st_supg_p.i1.Omega( stabil.delta, v, b, p )
= 0""",
'incompressibility' :
""" dw_stokes.i1.Omega( u, q )
+ dw_st_pspg_c.i1.Omega( stabil.tau, q, b, u )
+ dw_st_pspg_p.i1.Omega( stabil.tau, q, p )
= 0""",
}
solver_1 = {
'name' : 'oseen',
'kind' : 'nls.oseen',
'stabil_mat' : 'stabil',
'adimensionalize' : False,
'check_navier_stokes_residual' : False,
'i_max' : 10,
'eps_a' : 1e-8,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
'macheps' : 1e-16,
'lin_red' : 1e-2, # Linear system error < (eps_a * lin_red).
# Uncomment the following to get a convergence log.
## 'log' : {'text' : 'oseen_log.txt',
## 'plot' : 'oseen_log.png'},
}
solver_2 = {
'name' : 'ls',
'kind' : 'ls.scipy_direct',
}
##
# Functions.
import os.path as op
import sys
sys.path.append(data_dir) # Make installed example work.
import sfepy.examples.navier_stokes.utils as utils
cinc_name = 'cinc_' + op.splitext(op.basename(filename_mesh))[0]
cinc = getattr(utils, cinc_name)
name_map = {'p' : 'p', 'q' : 'q', 'u' : 'u', 'b' : 'b', 'v' : 'v',
'fluid' : 'fluid', 'omega' : 'omega', 'i1' : 'i1', 'i2' : 'i2',
'viscosity' : 'viscosity', 'velocity' : 'velocity',
'gamma' : 'gamma', 'delta' : 'delta', 'tau' : 'tau'}
functions = {
'cinc0' : (lambda coors, domain=None: cinc(coors, 0),),
'cinc1' : (lambda coors, domain=None: cinc(coors, 1),),
'stabil' : (StabilizationFunction(name_map),),
}