multi_physics/thermal_electric.py¶
Description
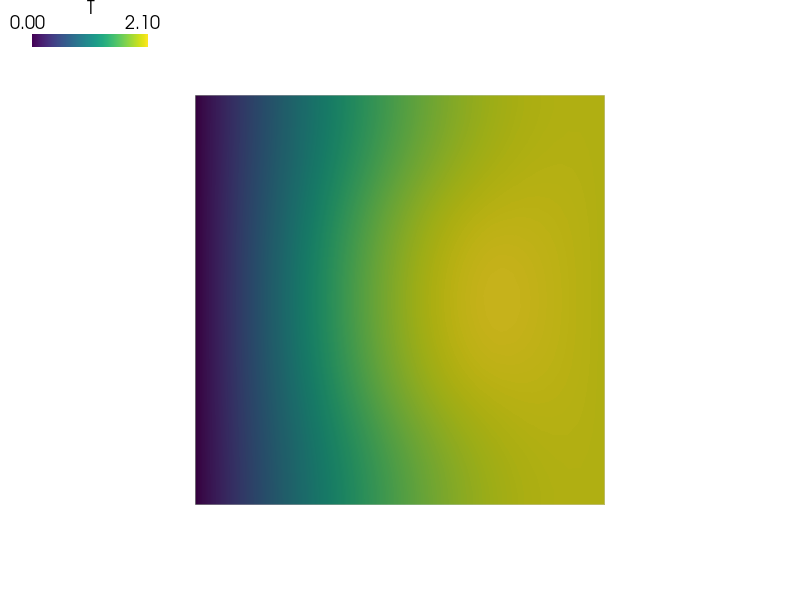
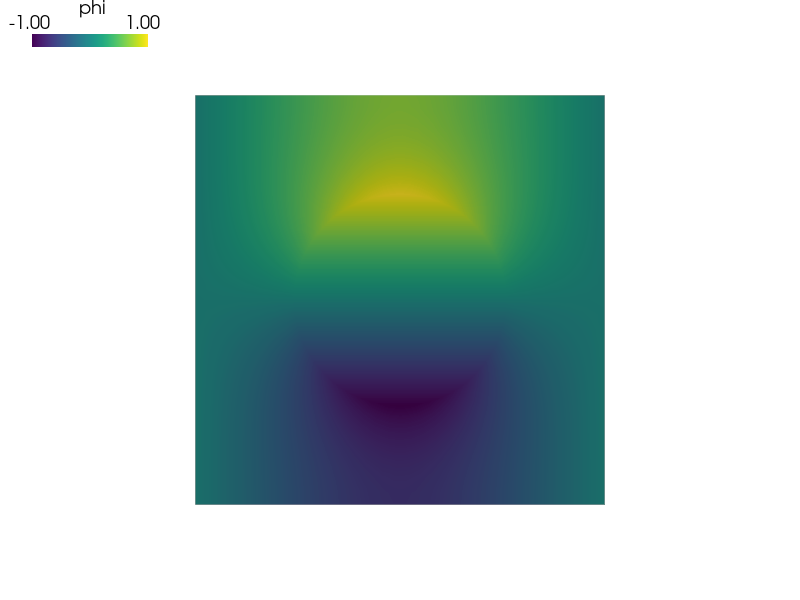
First solve the stationary electric conduction problem. Then use its results to solve the evolutionary heat conduction problem.
Run this example as on a command line:
$ python <path_to_this_file>/thermal_electric.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
First solve the stationary electric conduction problem. Then use its
results to solve the evolutionary heat conduction problem.
Run this example as on a command line::
$ python <path_to_this_file>/thermal_electric.py
"""
import sys
sys.path.append( '.' )
import os
from sfepy import data_dir
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/2d/special/circle_in_square.mesh'
# Time stepping for the heat conduction problem.
t0 = 0.0
t1 = 0.5
n_step = 11
# Material parameters.
specific_heat = 1.2
##########
cwd = os.path.split(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), __file__))[0]
options = {
'absolute_mesh_path' : True,
'output_dir' : os.path.join(cwd, 'output')
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Omega1' : 'cells of group 1',
'Omega2' : 'cells of group 2',
'Omega2_Surface': ('r.Omega1 *v r.Omega2', 'facet'),
'Left' : ('vertices in (x < %f)' % -0.4999, 'facet'),
'Right' : ('vertices in (x > %f)' % 0.4999, 'facet'),
}
materials = {
'm' : ({
'thermal_conductivity' : 2.0,
'electric_conductivity' : 1.5,
},),
}
# The fields use the same approximation, so a single field could be used
# instead.
fields = {
'temperature': ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
'potential' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'T' : ('unknown field', 'temperature', 0, 1),
's' : ('test field', 'temperature', 'T'),
'phi' : ('unknown field', 'potential', 1),
'psi' : ('test field', 'potential', 'phi'),
'phi_known' : ('parameter field', 'potential', '(set-to-None)'),
}
ics = {
'ic' : ('Omega', {'T.0' : 0.0}),
}
ebcs = {
'left' : ('Left', {'T.0' : 0.0, 'phi.0' : 0.0}),
'right' : ('Right', {'T.0' : 2.0, 'phi.0' : 0.0}),
'inside' : ('Omega2_Surface', {'phi.0' : 'set_electric_bc'}),
}
def set_electric_bc(coor):
y = coor[:,1]
ymin, ymax = y.min(), y.max()
val = 2.0 * (((y - ymin) / (ymax - ymin)) - 0.5)
return val
functions = {
'set_electric_bc' : (lambda ts, coor, bc, problem, **kwargs:
set_electric_bc(coor),),
}
equations = {
'2' : """%.12e * dw_dot.2.Omega( s, dT/dt )
+ dw_laplace.2.Omega( m.thermal_conductivity, s, T )
= dw_electric_source.2.Omega( m.electric_conductivity,
s, phi_known ) """ % specific_heat,
'1' : """dw_laplace.2.Omega( m.electric_conductivity, psi, phi ) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'problem' : 'nonlinear',
}),
'ts' : ('ts.simple', {
't0' : t0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : None,
'n_step' : n_step, # has precedence over dt!
'verbose' : 1,
}),
}
def main():
from sfepy.base.base import output
from sfepy.base.conf import ProblemConf, get_standard_keywords
from sfepy.discrete import Problem
output.prefix = 'therel:'
required, other = get_standard_keywords()
conf = ProblemConf.from_file(__file__, required, other)
problem = Problem.from_conf(conf, init_equations=False)
# Setup output directory according to options above.
problem.setup_default_output()
# First solve the stationary electric conduction problem.
problem.set_equations({'eq' : conf.equations['1']})
state_el = problem.solve()
problem.save_state(problem.get_output_name(suffix = 'el'), state_el)
# Then solve the evolutionary heat conduction problem, using state_el.
problem.set_equations({'eq' : conf.equations['2']})
phi_var = problem.get_variables()['phi_known']
phi_var.set_data(state_el())
problem.solve()
output('results saved in %s' % problem.get_output_name(suffix = '*'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()