diffusion/poisson_neumann.py¶
Description
The Poisson equation with Neumann boundary conditions on a part of the boundary.
Find 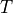 such that:
such that:
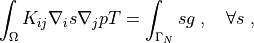
where 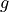 is the given flux,
is the given flux, 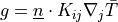 , and
, and 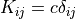 (an isotropic medium). See the
tutorial section Strong form of Poisson’s equation and its integration for a detailed explanation.
(an isotropic medium). See the
tutorial section Strong form of Poisson’s equation and its integration for a detailed explanation.
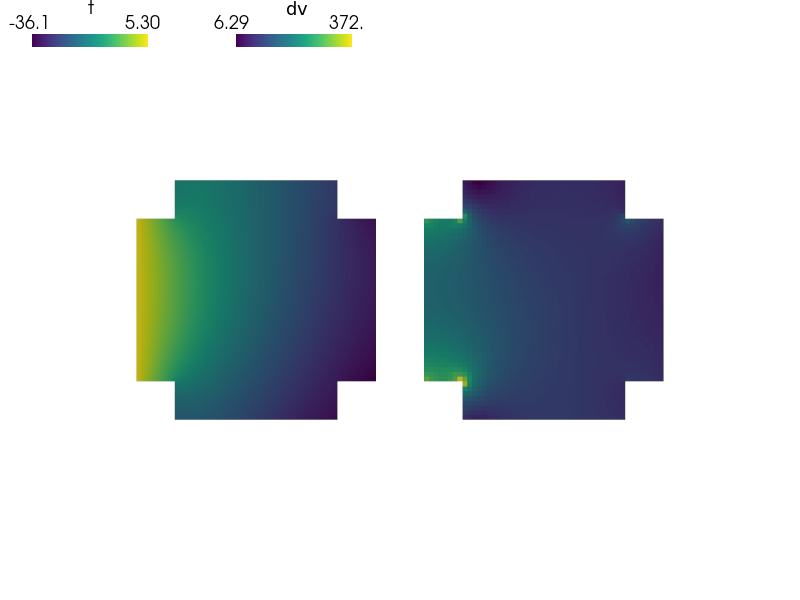
The diffusion velocity and fluxes through various parts of the boundary are
computed in the post_process() function. On ‘Gamma_N’ (the Neumann
condition boundary part), the flux/length should correspond to the given value
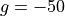 , while on ‘Gamma_N0’ the flux should be zero. Use the
‘refinement_level’ option (see the usage examples below) to check the
convergence of the numerical solution to those values. The total flux and the
flux through ‘Gamma_D’ (the Dirichlet condition boundary part) are shown as
well.
, while on ‘Gamma_N0’ the flux should be zero. Use the
‘refinement_level’ option (see the usage examples below) to check the
convergence of the numerical solution to those values. The total flux and the
flux through ‘Gamma_D’ (the Dirichlet condition boundary part) are shown as
well.
Usage Examples¶
Run with the default settings (no refinement):
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/diffusion/poisson_neumann.py
Refine the mesh twice:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/diffusion/poisson_neumann.py -O "'refinement_level' : 2"
r"""
The Poisson equation with Neumann boundary conditions on a part of the
boundary.
Find :math:`T` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} K_{ij} \nabla_i s \nabla_j p T
= \int_{\Gamma_N} s g
\;, \quad \forall s \;,
where :math:`g` is the given flux, :math:`g = \ul{n} \cdot K_{ij} \nabla_j
\bar{T}`, and :math:`K_{ij} = c \delta_{ij}` (an isotropic medium). See the
tutorial section :ref:`poisson-weak-form-tutorial` for a detailed explanation.
The diffusion velocity and fluxes through various parts of the boundary are
computed in the :func:`post_process()` function. On 'Gamma_N' (the Neumann
condition boundary part), the flux/length should correspond to the given value
:math:`g = -50`, while on 'Gamma_N0' the flux should be zero. Use the
'refinement_level' option (see the usage examples below) to check the
convergence of the numerical solution to those values. The total flux and the
flux through 'Gamma_D' (the Dirichlet condition boundary part) are shown as
well.
Usage Examples
--------------
Run with the default settings (no refinement)::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/diffusion/poisson_neumann.py
Refine the mesh twice::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/diffusion/poisson_neumann.py -O "'refinement_level' : 2"
"""
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import output, Struct
from sfepy import data_dir
def post_process(out, pb, state, extend=False):
"""
Calculate :math:`\nabla t` and compute boundary fluxes.
"""
dv = pb.evaluate('ev_diffusion_velocity.i.Omega(m.K, t)', mode='el_avg',
verbose=False)
out['dv'] = Struct(name='output_data', mode='cell',
data=dv, dofs=None)
totals = nm.zeros(3)
for gamma in ['Gamma_N', 'Gamma_N0', 'Gamma_D']:
flux = pb.evaluate('ev_surface_flux.i.%s(m.K, t)' % gamma,
verbose=False)
area = pb.evaluate('ev_volume.i.%s(t)' % gamma, verbose=False)
flux_data = (gamma, flux, area, flux / area)
totals += flux_data[1:]
output('%8s flux: % 8.3f length: % 8.3f flux/length: % 8.3f'
% flux_data)
totals[2] = totals[0] / totals[1]
output(' total flux: % 8.3f length: % 8.3f flux/length: % 8.3f'
% tuple(totals))
return out
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/2d/cross-51-0.34.mesh'
materials = {
'flux' : ({'val' : -50.0},),
'm' : ({'K' : 2.7 * nm.eye(2)},),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Gamma_D' : ('vertices in (x < -0.4999)', 'facet'),
'Gamma_N0' : ('vertices in (y > 0.4999)', 'facet'),
'Gamma_N' : ('vertices of surface -s (r.Gamma_D +v r.Gamma_N0)',
'facet'),
}
fields = {
'temperature' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
't' : ('unknown field', 'temperature', 0),
's' : ('test field', 'temperature', 't'),
}
ebcs = {
't1' : ('Gamma_D', {'t.0' : 5.3}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2
}
equations = {
'Temperature' : """
dw_diffusion.i.Omega(m.K, s, t)
= dw_integrate.i.Gamma_N(flux.val, s)
"""
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
}),
}
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
'refinement_level' : 0,
'post_process_hook' : 'post_process',
}