acoustics/acoustics.py¶
Description
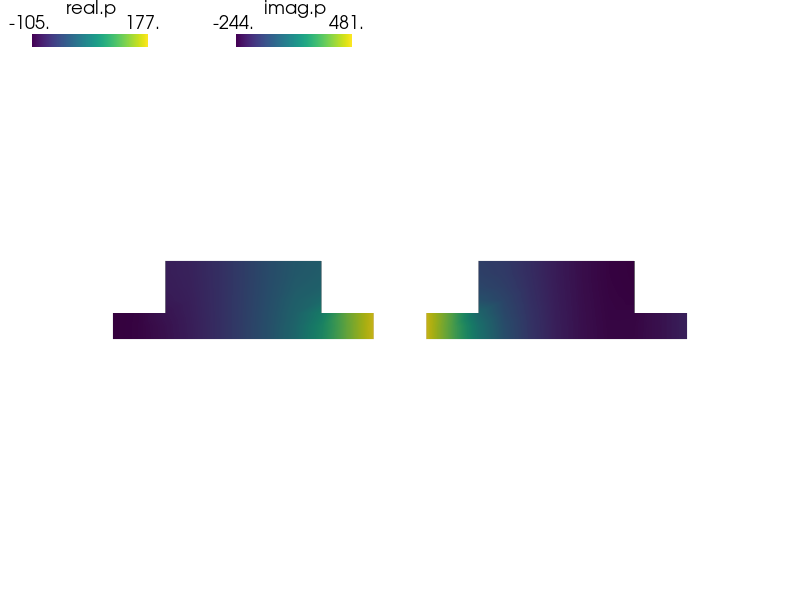
Acoustic pressure distribution.
This example shows how to solve a problem in complex numbers, note the ‘accoustic_pressure’ field definition.
Find 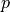 such that:
such that:
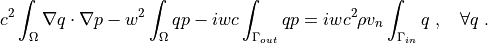
r"""
Acoustic pressure distribution.
This example shows how to solve a problem in complex numbers, note the
'accoustic_pressure' field definition.
Find :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
c^2 \int_{\Omega} \nabla q \cdot \nabla p
- w^2 \int_{\Omega} q p
- i w c \int_{\Gamma_{out}} q p
= i w c^2 \rho v_n \int_{\Gamma_{in}} q
\;, \quad \forall q \;.
"""
from sfepy import data_dir
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/2d/special/two_rectangles.mesh'
v_n = 1.0 # m/s
w = 1000.0
c = 343.0 # m/s
rho = 1.55 # kg/m^3
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
}
materials = {
'one' : ({'one' : 1.0},),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Gamma_in' : ('vertices in (x < 0.01)', 'facet'),
'Gamma_out' : ('vertices in (x > 0.99)', 'facet'),
}
fields = {
'accoustic_pressure' : ('complex', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'p' : ('unknown field', 'accoustic_pressure', 0),
'q' : ('test field', 'accoustic_pressure', 'p'),
}
ebcs = {
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2,
}
equations = {
'Acoustic pressure' :
"""%s * dw_laplace.i.Omega( one.one, q, p )
- %s * dw_dot.i.Omega( q, p )
- %s * dw_dot.i.Gamma_out( q, p )
= %s * dw_integrate.i.Gamma_in( q )"""
% (c*c, w*w, 1j*w*c, 1j*w*c*c*rho*v_n)
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-1,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
'macheps' : 1e-16,
'lin_red' : 1e-1, # Linear system error < (eps_a * lin_red).
'ls_red' : 0.1,
'ls_red_warp' : 0.001,
'ls_on' : 1.1,
'ls_min' : 1e-5,
'check' : 0,
'delta' : 1e-6,
})
}