navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc.py¶
Description
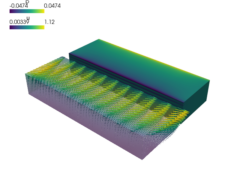
Incompressible Stokes flow with Navier (slip) boundary conditions, flow driven by a moving wall and a small diffusion for stabilization.
This example demonstrates the use of no-penetration boundary conditions as well as edge direction boundary conditions together with Navier or slip boundary conditions.
Find 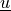 ,
, 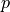 such that:
such that:
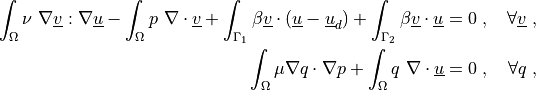
where 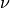 is the fluid viscosity,
is the fluid viscosity, 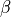 is the slip
coefficient,
is the slip
coefficient, 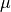 is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
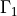 is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
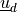 and
and 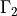 are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both
are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both 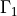 ,
, 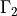 and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
The no-penetration boundary conditions are applied on 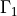 ,
,
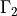 , except the vertices of the block edges, where the edge
direction boundary conditions are applied. Optionally, Dirichlet boundary
conditions can be applied on the inlet, see the code below.
, except the vertices of the block edges, where the edge
direction boundary conditions are applied. Optionally, Dirichlet boundary
conditions can be applied on the inlet, see the code below.
The mesh is created by gen_block_mesh() function - try different mesh
dimensions and resolutions below. For large meshes use the 'ls_i' linear
solver - PETSc + petsc4py is needed in that case.
See also navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc_penalty.py.
r"""
Incompressible Stokes flow with Navier (slip) boundary conditions, flow driven
by a moving wall and a small diffusion for stabilization.
This example demonstrates the use of `no-penetration` boundary conditions as
well as `edge direction` boundary conditions together with Navier or slip
boundary conditions.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \nu\ \nabla \ul{v} : \nabla \ul{u}
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v}
+ \int_{\Gamma_1} \beta \ul{v} \cdot (\ul{u} - \ul{u}_d)
+ \int_{\Gamma_2} \beta \ul{v} \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\int_{\Omega} \mu \nabla q \cdot \nabla p
+ \int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;,
where :math:`\nu` is the fluid viscosity, :math:`\beta` is the slip
coefficient, :math:`\mu` is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
:math:`\Gamma_1` is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
:math:`\ul{u}_d` and :math:`\Gamma_2` are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both :math:`\Gamma_1`, :math:`\Gamma_2` and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
The `no-penetration` boundary conditions are applied on :math:`\Gamma_1`,
:math:`\Gamma_2`, except the vertices of the block edges, where the `edge
direction` boundary conditions are applied. Optionally, Dirichlet boundary
conditions can be applied on the inlet, see the code below.
The mesh is created by ``gen_block_mesh()`` function - try different mesh
dimensions and resolutions below. For large meshes use the ``'ls_i'`` linear
solver - PETSc + petsc4py is needed in that case.
See also :ref:`navier_stokes-stokes_slip_bc_penalty`.
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.discrete.fem.meshio import UserMeshIO
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
from sfepy.homogenization.utils import define_box_regions
# Mesh dimensions.
dims = nm.array([3, 1, 0.5])
# Mesh resolution: increase to improve accuracy.
shape = [11, 15, 15]
def mesh_hook(mesh, mode):
"""
Generate the block mesh.
"""
if mode == 'read':
mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, [0, 0, 0], name='user_block',
verbose=False)
return mesh
elif mode == 'write':
pass
filename_mesh = UserMeshIO(mesh_hook)
regions = define_box_regions(3, 0.5 * dims)
regions.update({
'Omega' : 'all',
'Edges_v' : ("""(r.Near *v r.Bottom) +v
(r.Bottom *v r.Far) +v
(r.Far *v r.Top) +v
(r.Top *v r.Near)""", 'edge'),
'Gamma1_f' : ('copy r.Top', 'face'),
'Gamma2_f' : ('r.Near +v r.Bottom +v r.Far', 'face'),
'Gamma_f' : ('r.Gamma1_f +v r.Gamma2_f', 'face'),
'Gamma_v' : ('r.Gamma_f -v r.Edges_v', 'face'),
'Inlet_f' : ('r.Left -v r.Gamma_f', 'face'),
})
fields = {
'velocity' : ('real', 3, 'Omega', 1),
'pressure' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
def get_u_d(ts, coors, region=None):
"""
Given stator velocity.
"""
out = nm.zeros_like(coors)
out[:] = [1.0, 1.0, 0.0]
return out
functions = {
'get_u_d' : (get_u_d,),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'velocity', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'velocity', 'u'),
'u_d' : ('parameter field', 'velocity',
{'setter' : 'get_u_d'}),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure', 1),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
# Try setting the inlet velocity by un-commenting the 'inlet' ebcs.
ebcs = {
## 'inlet' : ('Inlet_f', {'u.0' : 1.0, 'u.[1, 2]' : 0.0}),
}
lcbcs = {
'walls' : ('Gamma_v', {'u.all' : None}, None, 'no_penetration',
'normals_Gamma.vtk'),
'edges' : ('Edges_v', [(-0.5, 1.5)], {'u.all' : None}, None,
'edge_direction', 'edges_Edges.vtk'),
}
materials = {
'm' : ({
'nu' : 1e-3,
'beta' : 1e-2,
'mu' : 1e-10,
},),
}
equations = {
'balance' :
"""dw_div_grad.5.Omega(m.nu, v, u)
- dw_stokes.5.Omega(v, p)
+ dw_surface_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ dw_surface_dot.5.Gamma2_f(m.beta, v, u)
=
+ dw_surface_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u_d)""",
'incompressibility' :
"""dw_laplace.5.Omega(m.mu, q, p)
+ dw_stokes.5.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'ls_d' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'ls_i' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : 'bcgsl', # ksp_type
'precond' : 'bjacobi', # pc_type
'sub_precond' : 'ilu', # sub_pc_type
'eps_a' : 0.0, # abstol
'eps_r' : 1e-12, # rtol
'eps_d' : 1e10, # Divergence tolerance.
'i_max' : 2500, # maxits
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
}),
}
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls_d',
}

