diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py¶
Description
Example of solving Laplace’s equation on a block domain refined with level 1 hanging nodes.
The domain is progressively refined towards the edge/face of the block, where Dirichlet boundary conditions are prescribed by an oscillating function.
Find 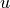 such that:
such that:
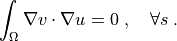
Notes¶
The implementation of the mesh refinement with level 1 hanging nodes is a proof-of-concept code with many unresolved issues. The main problem is the fact that a user needs to input the cells to refine at each level, while taking care of the following constraints:
the level 1 hanging nodes constraint: a cell that has a less-refined neighbour cannot be refined;
the implementation constraint: a cell with a refined neighbour cannot be refined.
The hanging nodes are treated by a basis transformation/DOF substitution, which has to be applied explicitly by the user:
call
field.substitute_dofs(subs)before assembling and solving;then call
field.restore_dofs()before saving results.
Usage Examples¶
Default options, 2D, storing results in ‘output’ directory:
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
Default options, 3D, storing results in ‘output’ directory:
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py -3 output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b --3d
Finer initial domain, 2D, storing results in ‘output’ directory:
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py --shape=11,11 output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
Bi-quadratic approximation, 2D, storing results in ‘output’ directory:
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py --order=2 output
# View solution with higher order DOFs removed.
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
# View full solution on a mesh adapted for visualization.
$ python postproc.py output/hanging_u.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
#!/usr/bin/env python
r"""
Example of solving Laplace's equation on a block domain refined with level 1
hanging nodes.
The domain is progressively refined towards the edge/face of the block, where
Dirichlet boundary conditions are prescribed by an oscillating function.
Find :math:`u` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \nabla v \cdot \nabla u = 0
\;, \quad \forall s \;.
Notes
-----
The implementation of the mesh refinement with level 1 hanging nodes is a
proof-of-concept code with many unresolved issues. The main problem is the fact
that a user needs to input the cells to refine at each level, while taking care
of the following constraints:
- the level 1 hanging nodes constraint: a cell that has a less-refined
neighbour cannot be refined;
- the implementation constraint: a cell with a refined neighbour cannot be
refined.
The hanging nodes are treated by a basis transformation/DOF substitution, which
has to be applied explicitly by the user:
- call ``field.substitute_dofs(subs)`` before assembling and solving;
- then call ``field.restore_dofs()`` before saving results.
Usage Examples
--------------
Default options, 2D, storing results in 'output' directory::
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
Default options, 3D, storing results in 'output' directory::
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py -3 output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b --3d
Finer initial domain, 2D, storing results in 'output' directory::
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py --shape=11,11 output
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
Bi-quadratic approximation, 2D, storing results in 'output' directory::
$ python examples/diffusion/laplace_refine_interactive.py --order=2 output
# View solution with higher order DOFs removed.
$ python postproc.py output/hanging.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
# View full solution on a mesh adapted for visualization.
$ python postproc.py output/hanging_u.vtk --wireframe -b -d'u,plot_warp_scalar'
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from argparse import RawDescriptionHelpFormatter, ArgumentParser
import os
import sys
sys.path.append('.')
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import output, Struct
from sfepy.base.ioutils import ensure_path
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
from sfepy.discrete import (FieldVariable, Integral, Equation, Equations,
Function, Problem)
from sfepy.discrete.fem import FEDomain, Field
from sfepy.discrete.conditions import (Conditions, EssentialBC)
import sfepy.discrete.fem.refine_hanging as rh
from sfepy.solvers.ls import ScipyDirect
from sfepy.solvers.nls import Newton
from sfepy.terms import Term
def refine_towards_facet(domain0, grading, axis):
subs = None
domain = domain0
for level, coor in enumerate(grading):
refine = nm.zeros(domain.mesh.n_el, dtype=nm.uint8)
region = domain.create_region('aux',
'vertices in (%s %.10f)' % (axis, coor),
add_to_regions=False)
refine[region.cells] = 1
domain, subs = rh.refine(domain, refine, subs=subs)
return domain, subs
helps = {
'output_dir' :
'output directory',
'dims' :
'dimensions of the block [default: %(default)s]',
'shape' :
'shape (counts of nodes in x, y[, z]) of the block [default: %(default)s]',
'centre' :
'centre of the block [default: %(default)s]',
'3d' :
'generate a 3D block',
'order' :
'field approximation order',
}
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(description=__doc__.rstrip(),
formatter_class=RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('output_dir', help=helps['output_dir'])
parser.add_argument('--dims', metavar='dims',
action='store', dest='dims',
default='1.0,1.0,1.0', help=helps['dims'])
parser.add_argument('--shape', metavar='shape',
action='store', dest='shape',
default='7,7,7', help=helps['shape'])
parser.add_argument('--centre', metavar='centre',
action='store', dest='centre',
default='0.0,0.0,0.0', help=helps['centre'])
parser.add_argument('-3', '--3d',
action='store_true', dest='is_3d',
default=False, help=helps['3d'])
parser.add_argument('--order', metavar='int', type=int,
action='store', dest='order',
default=1, help=helps['order'])
options = parser.parse_args()
dim = 3 if options.is_3d else 2
dims = nm.array(eval(options.dims), dtype=nm.float64)[:dim]
shape = nm.array(eval(options.shape), dtype=nm.int32)[:dim]
centre = nm.array(eval(options.centre), dtype=nm.float64)[:dim]
output('dimensions:', dims)
output('shape: ', shape)
output('centre: ', centre)
mesh0 = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, centre, name='block-fem',
verbose=True)
domain0 = FEDomain('d', mesh0)
bbox = domain0.get_mesh_bounding_box()
min_x, max_x = bbox[:, 0]
eps = 1e-8 * (max_x - min_x)
cnt = (shape[0] - 1) // 2
g0 = 0.5 * dims[0]
grading = nm.array([g0 / 2**ii for ii in range(cnt)]) + eps + centre[0] - g0
domain, subs = refine_towards_facet(domain0, grading, 'x <')
omega = domain.create_region('Omega', 'all')
gamma1 = domain.create_region('Gamma1',
'vertices in (x < %.10f)' % (min_x + eps),
'facet')
gamma2 = domain.create_region('Gamma2',
'vertices in (x > %.10f)' % (max_x - eps),
'facet')
field = Field.from_args('fu', nm.float64, 1, omega,
approx_order=options.order)
if subs is not None:
field.substitute_dofs(subs)
u = FieldVariable('u', 'unknown', field)
v = FieldVariable('v', 'test', field, primary_var_name='u')
integral = Integral('i', order=2*options.order)
t1 = Term.new('dw_laplace(v, u)',
integral, omega, v=v, u=u)
eq = Equation('eq', t1)
eqs = Equations([eq])
def u_fun(ts, coors, bc=None, problem=None):
"""
Define a displacement depending on the y coordinate.
"""
if coors.shape[1] == 2:
min_y, max_y = bbox[:, 1]
y = (coors[:, 1] - min_y) / (max_y - min_y)
val = (max_y - min_y) * nm.cos(3 * nm.pi * y)
else:
min_y, max_y = bbox[:, 1]
min_z, max_z = bbox[:, 2]
y = (coors[:, 1] - min_y) / (max_y - min_y)
z = (coors[:, 2] - min_z) / (max_z - min_z)
val = ((max_y - min_y) * (max_z - min_z)
* nm.cos(3 * nm.pi * y) * (1.0 + 3.0 * (z - 0.5)**2))
return val
bc_fun = Function('u_fun', u_fun)
fix1 = EssentialBC('shift_u', gamma1, {'u.0' : bc_fun})
fix2 = EssentialBC('fix2', gamma2, {'u.all' : 0.0})
ls = ScipyDirect({})
nls = Newton({}, lin_solver=ls)
pb = Problem('heat', equations=eqs)
pb.set_bcs(ebcs=Conditions([fix1, fix2]))
pb.set_solver(nls)
state = pb.solve(save_results=False)
if subs is not None:
field.restore_dofs()
filename = os.path.join(options.output_dir, 'hanging.vtk')
ensure_path(filename)
pb.save_state(filename, state)
if options.order > 1:
pb.save_state(filename, state, linearization=Struct(kind='adaptive',
min_level=0,
max_level=8,
eps=1e-3))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()

