multi_physics/thermo_elasticity_ess.py¶
Description
Thermo-elasticity with a computed temperature demonstrating equation sequence solver.
Uses dw_biot term with an isotropic coefficient for thermo-elastic coupling.
The equation sequence solver ('ess' in solvers) automatically solves
first the temperature distribution and then the elasticity problem with the
already computed temperature.
Find 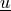 ,
, 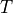 such that:
such that:
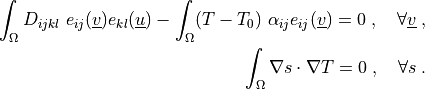
where
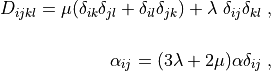
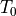 is the background temperature and
is the background temperature and 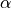 is the thermal
expansion coefficient.
is the thermal
expansion coefficient.
Notes¶
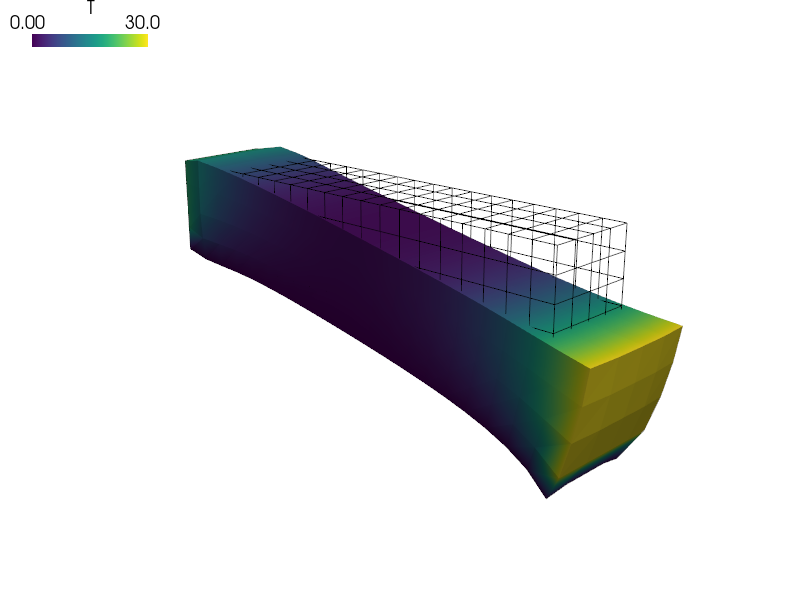
The gallery image was produced by (plus proper view settings):
sfepy-view block.vtk -f T:p1 u:wu:f1000:p0 u:vw:p0
r"""
Thermo-elasticity with a computed temperature demonstrating equation sequence
solver.
Uses `dw_biot` term with an isotropic coefficient for thermo-elastic coupling.
The equation sequence solver (``'ess'`` in ``solvers``) automatically solves
first the temperature distribution and then the elasticity problem with the
already computed temperature.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`T` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
- \int_{\Omega} (T - T_0)\ \alpha_{ij} e_{ij}(\ul{v})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\int_{\Omega} \nabla s \cdot \nabla T
= 0
\;, \quad \forall s \;.
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;, \\
\alpha_{ij} = (3 \lambda + 2 \mu) \alpha \delta_{ij} \;,
:math:`T_0` is the background temperature and :math:`\alpha` is the thermal
expansion coefficient.
Notes
-----
The gallery image was produced by (plus proper view settings)::
sfepy-view block.vtk -f T:p1 u:wu:f1000:p0 u:vw:p0
"""
import numpy as np
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_lame
from sfepy import data_dir
# Material parameters.
lam = 10.0
mu = 5.0
thermal_expandability = 1.25e-5
T0 = 20.0 # Background temperature.
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/block.mesh'
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
'block_solve' : True,
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Left' : ('vertices in (x < -4.99)', 'facet'),
'Right' : ('vertices in (x > 4.99)', 'facet'),
'Bottom' : ('vertices in (z < -0.99)', 'facet'),
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 3, 'Omega', 1),
'temperature': ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
'T' : ('unknown field', 'temperature', 1),
's' : ('test field', 'temperature', 'T'),
}
ebcs = {
'u0' : ('Left', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
't0' : ('Left', {'T.0' : 20.0}),
't2' : ('Bottom', {'T.0' : 0.0}),
't1' : ('Right', {'T.0' : 30.0}),
}
eye_sym = np.array([[1], [1], [1], [0], [0], [0]], dtype=np.float64)
materials = {
'solid' : ({
'D' : stiffness_from_lame(3, lam=lam, mu=mu),
'alpha' : (3.0 * lam + 2.0 * mu) * thermal_expandability * eye_sym
},),
}
equations = {
'balance_of_forces' : """
+ dw_lin_elastic.2.Omega(solid.D, v, u)
- dw_biot.2.Omega(solid.alpha, v, T)
= 0
""",
'temperature' : """
+ dw_laplace.1.Omega(s, T)
= 0
"""
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
}),
}