linear_elasticity/material_nonlinearity.py¶
Description
Example demonstrating how a linear elastic term can be used to solve an elasticity problem with a material nonlinearity.
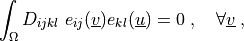
where
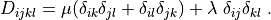
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
r"""
Example demonstrating how a linear elastic term can be used to solve an
elasticity problem with a material nonlinearity.
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
"""
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.linalg import norm_l2_along_axis
from sfepy import data_dir
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_lame
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/cylinder.mesh'
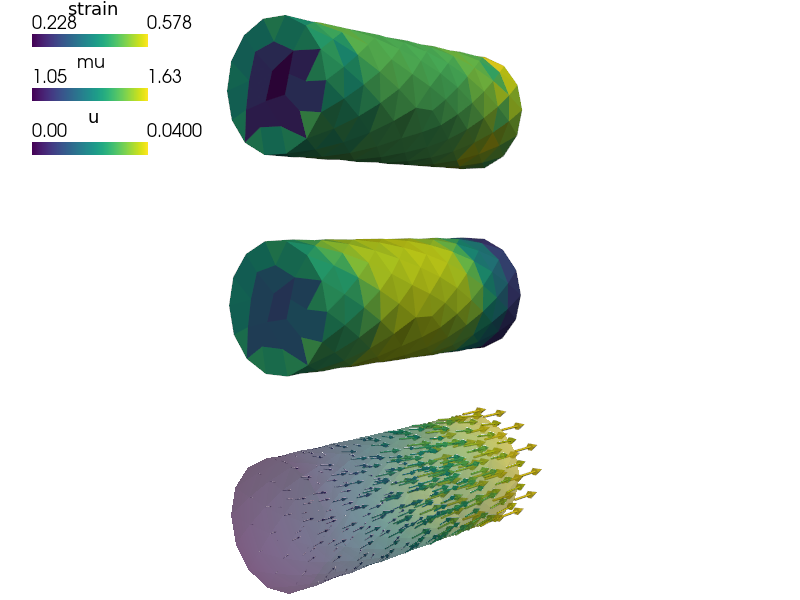
def post_process(out, pb, state, extend=False):
from sfepy.base.base import Struct
mu = pb.evaluate('ev_integrate_mat.2.Omega(nonlinear.mu, u)',
mode='el_avg', copy_materials=False, verbose=False)
out['mu'] = Struct(name='mu', mode='cell', data=mu, dofs=None)
strain = pb.evaluate('ev_cauchy_strain.2.Omega(u)', mode='el_avg')
out['strain'] = Struct(name='strain', mode='cell', data=strain, dofs=None)
return out
strains = [None]
def get_pars(ts, coors, mode='qp',
equations=None, term=None, problem=None, **kwargs):
"""
The material nonlinearity function - the Lamé coefficient `mu`
depends on the strain.
"""
if mode != 'qp': return
val = nm.empty(coors.shape[0], dtype=nm.float64)
val.fill(1e0)
order = term.integral.order
uvar = equations.variables['u']
strain = problem.evaluate('ev_cauchy_strain.%d.Omega(u)' % order,
u=uvar, mode='qp')
if ts.step > 0:
strain0 = strains[-1]
else:
strain0 = strain
dstrain = (strain - strain0) / ts.dt
dstrain.shape = (strain.shape[0] * strain.shape[1], strain.shape[2])
norm = norm_l2_along_axis(dstrain)
val += norm
# Store history.
strains[0] = strain
return {'D': stiffness_from_lame(dim=3, lam=1e1, mu=val),
'mu': val.reshape(-1, 1, 1)}
def pull(ts, coors, **kwargs):
val = nm.empty_like(coors[:,0])
val.fill(0.01 * ts.step)
return val
functions = {
'get_pars' : (get_pars,),
'pull' : (pull,),
}
options = {
'ts' : 'ts',
'output_format' : 'h5',
'save_times' : 'all',
'post_process_hook' : 'post_process',
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Left' : ('vertices in (x < 0.001)', 'facet'),
'Right' : ('vertices in (x > 0.099)', 'facet'),
}
materials = {
'nonlinear' : 'get_pars',
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
}
ebcs = {
'Fixed' : ('Left', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
'Displaced' : ('Right', {'u.0' : 'pull', 'u.[1,2]' : 0.0}),
}
equations = {
'balance_of_forces in time' :
"""dw_lin_elastic.2.Omega(nonlinear.D, v, u) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton',
{'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
}),
'ts' : ('ts.simple',
{'t0' : 0.0,
't1' : 1.0,
'dt' : None,
'n_step' : 5,
'quasistatic' : True,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
}