linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_probes.py¶
Description
This example shows how to use the post_process_hook to probe the output data.
Find 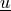 such that:
such that:
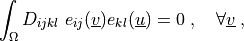
where
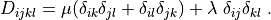
r"""
This example shows how to use the post_process_hook to probe the output data.
Find :math:`\ul{u}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
"""
from sfepy.examples.linear_elasticity.linear_elastic import *
import os
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import Struct
try:
from sfepy.postprocess.probes_vtk import Probe
except ImportError:
Probe = None
# Define options.
options = {
'output_dir' : '.',
'post_process_hook' : 'post_process',
}
# The function returning the probe parametrization.
def par_fun(idx):
return nm.log(idx + 1) / nm.log(20) * 0.04
# Define the function post_process, that will be called after the problem is
# solved.
def post_process(out, problem, variables, extend=False):
"""
This will be called after the problem is solved.
Parameters
----------
out : dict
The output dictionary, where this function will store additional data.
problem : Problem instance
The current Problem instance.
variables : Variables instance
The computed state, containing FE coefficients of all the unknown
variables.
extend : bool
The flag indicating whether to extend the output data to the whole
domain. It can be ignored if the problem is solved on the whole domain
already.
Returns
-------
out : dict
The updated output dictionary.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
# Cauchy strain averaged in elements.
strain = problem.evaluate('ev_cauchy_strain.i.Omega( u )',
mode='el_avg')
out['cauchy_strain'] = Struct(name='output_data',
mode='cell', data=strain,
dofs=None)
# Cauchy stress averaged in elements.
stress = problem.evaluate('ev_cauchy_stress.i.Omega( solid.D, u )',
mode='el_avg')
out['cauchy_stress'] = Struct(name='output_data',
mode='cell', data=stress,
dofs=None)
if Probe is None:
# Do not probe if vtk cannot be imported.
return out
# Define three line probes in axial directions.
mesh = problem.domain.mesh
bbox = mesh.get_bounding_box()
cx, cy, cz = 0.5 * bbox.sum(axis=0)
labels = []
probe_names = []
probe = Probe(out, mesh)
# line probe
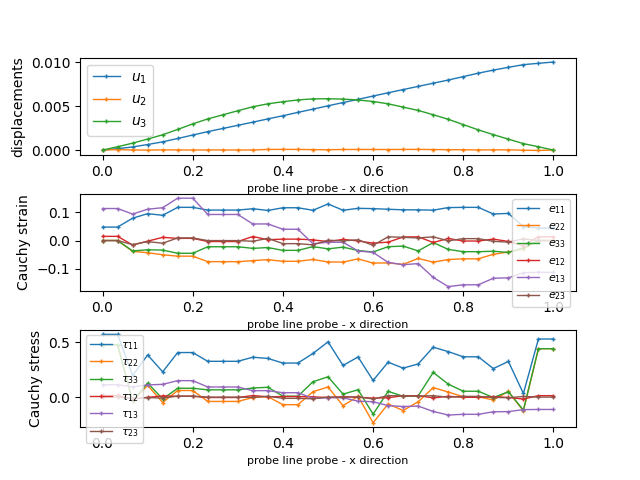
labels.append('line probe - x direction')
probe_names.append('line')
probe.add_line_probe('line',
[bbox[0,0], cy, cz],
[bbox[1,0], cy, cz],
30)
# circle probe
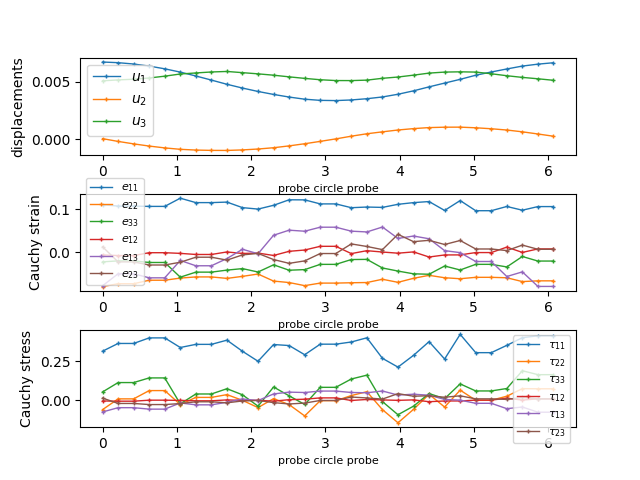
labels.append('circle probe')
probe_names.append('circle')
probe.add_circle_probe('circle',
[cx, cy, cz],
[0, 0, 1],
0.015,
30)
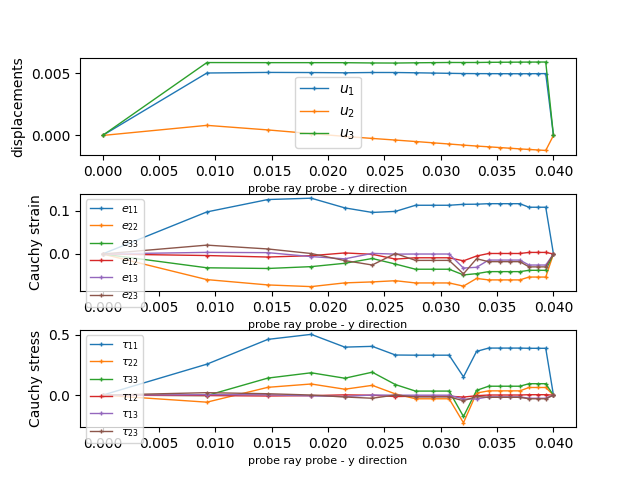
# ray probe
labels.append('ray probe - y direction')
probe_names.append('ray')
probe.add_ray_probe('ray',
[cx, bbox[0,1], cz],
[0, 1, 0],
par_fun, 20)
# Gnerate matplotlib figures with the probe plot.
for probe_name, label in zip(probe_names, labels):
fig = plt.figure()
plt.clf()
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.4)
plt.subplot(311)
pars, vals = probe(probe_name, 'u')
for ic in range(vals.shape[1]):
plt.plot(pars, vals[:,ic], label=r'$u_{%d}$' % (ic + 1),
lw=1, ls='-', marker='+', ms=3)
plt.ylabel('displacements')
plt.xlabel('probe %s' % label, fontsize=8)
plt.legend(loc='best', prop=fm.FontProperties(size=10))
sym_labels = ['11', '22', '33', '12', '13', '23']
plt.subplot(312)
pars, vals = probe(probe_name, 'cauchy_strain')
for ii, lab in enumerate(sym_labels):
plt.plot(pars, vals[:,ii], label=r'$e_{%s}$' % lab,
lw=1, ls='-', marker='+', ms=3)
plt.ylabel('Cauchy strain')
plt.xlabel('probe %s' % label, fontsize=8)
plt.legend(loc='best', prop=fm.FontProperties(size=8))
plt.subplot(313)
pars, vals = probe(probe_name, 'cauchy_stress')
for ii, lab in enumerate(sym_labels):
plt.plot(pars, vals[:,ii], label=r'$\tau_{%s}$' % lab,
lw=1, ls='-', marker='+', ms=3)
plt.ylabel('Cauchy stress')
plt.xlabel('probe %s' % label, fontsize=8)
plt.legend(loc='best', prop=fm.FontProperties(size=8))
opts = problem.conf.options
filename_results = os.path.join(opts.get('output_dir'),
'cylinder_probe_%s.png' % probe_name)
fig.savefig(filename_results)
return out