linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_up.py¶
Description
Nearly incompressible linear elasticity in mixed displacement-pressure formulation with comments.
Find 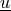 ,
, 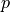 such that:
such that:
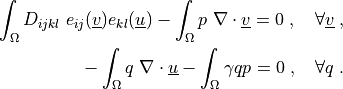
r"""
Nearly incompressible linear elasticity in mixed displacement-pressure
formulation with comments.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
- \int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u}
- \int_{\Omega} \gamma q p
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;.
"""
#!
#! Linear Elasticity
#! =================
#$ \centerline{Example input file, \today}
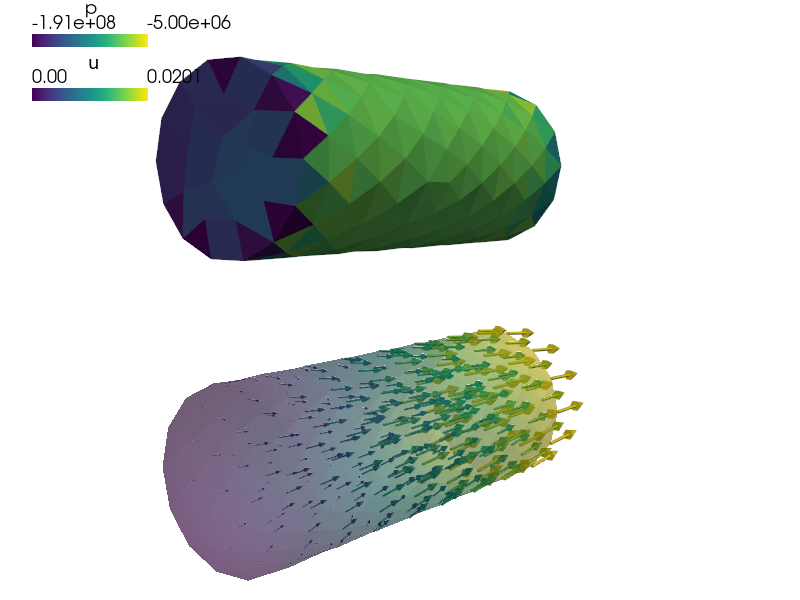
#! This file models a cylinder that is fixed at one end while the
#! second end has a specified displacement of 0.02 in the x direction
#! (this boundary condition is named PerturbedSurface).
#! The output is the displacement for each node, saved by default to
#! simple_out.vtk. The material is linear elastic.
from sfepy import data_dir
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_youngpoisson_mixed, bulk_from_youngpoisson
#! Mesh
#! ----
dim = 3
approx_u = '3_4_P1'
approx_p = '3_4_P0'
order = 2
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/cylinder.mesh'
#! Regions
#! -------
#! Whole domain 'Omega', left and right ends.
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Left' : ('vertices in (x < 0.001)', 'facet'),
'Right' : ('vertices in (x > 0.099)', 'facet'),
}
#! Materials
#! ---------
#! The linear elastic material model is used.
materials = {
'solid' : ({'D' : stiffness_from_youngpoisson_mixed(dim, 0.7e9, 0.4),
'gamma' : 1.0/bulk_from_youngpoisson(0.7e9, 0.4)},),
}
#! Fields
#! ------
#! A field is used to define the approximation on a (sub)domain
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
'pressure' : ('real', 'scalar', 'Omega', 0),
}
#! Integrals
#! ---------
#! Define the integral type Volume/Surface and quadrature rule.
integrals = {
'i' : order,
}
#! Variables
#! ---------
#! Define displacement and pressure fields and corresponding fields
#! for test variables.
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement'),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure'),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
#! Boundary Conditions
#! -------------------
#! The left end of the cylinder is fixed (all DOFs are zero) and
#! the 'right' end has non-zero displacements only in the x direction.
ebcs = {
'Fixed' : ('Left', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
'PerturbedSurface' : ('Right', {'u.0' : 0.02, 'u.1' : 0.0}),
}
#! Equations
#! ---------
#! The weak formulation of the linear elastic problem.
equations = {
'balance_of_forces' :
""" dw_lin_elastic.i.Omega( solid.D, v, u )
- dw_stokes.i.Omega( v, p )
= 0 """,
'pressure constraint' :
"""- dw_stokes.i.Omega( u, q )
- dw_dot.i.Omega( solid.gamma, q, p )
= 0""",
}
#! Solvers
#! -------
#! Define linear and nonlinear solver.
#! Even linear problems are solved by a nonlinear solver - only one
#! iteration is needed and the final residual is obtained for free.
solvers = {
'ls': ('ls.schur_mumps', {
'schur_variables': ['p'],
'fallback': 'ls2'
}),
'ls2': ('ls.scipy_umfpack', {'fallback': 'ls3'}),
'ls3': ('ls.scipy_superlu', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-2,
'eps_r' : 1e-10,
}),
}
#! Options
#! -------
#! Various problem-specific options.
options = {
'output_dir' : './output',
'absolute_mesh_path' : True,
}