linear_elasticity/elastic_contact_planes.py¶
Description
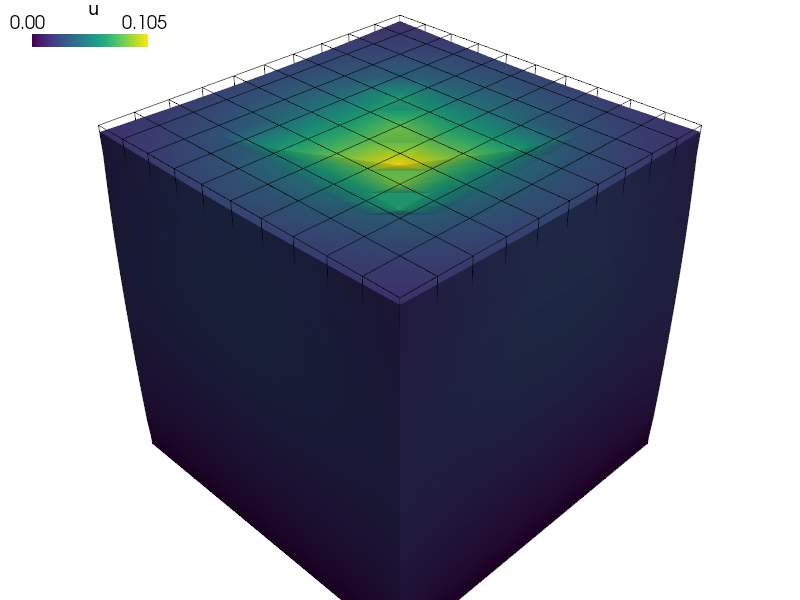
Elastic contact planes simulating an indentation test.
Four contact planes bounded by polygons (triangles in this case) form a very rigid pyramid shape simulating an indentor.
Find 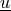 such that:
such that:
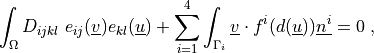
where
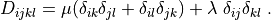
Notes¶
Even though the material is linear elastic and small deformations are used, the problem is highly nonlinear due to contacts with the planes.
Checking the tangent matrix by finite differences by setting ‘check’ in ‘nls’ solver configuration to nonzero is rather tricky - the active contact points must not change during the test. This can be ensured by a sufficient initial penetration and large enough contact boundary polygons (hard!), or by tweaking the dw_contact_plane term to mask points only by undeformed coordinates.
r"""
Elastic contact planes simulating an indentation test.
Four contact planes bounded by polygons (triangles in this case) form a very
rigid pyramid shape simulating an indentor.
Find :math:`\ul{u}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
+ \sum_{i=1}^4 \int_{\Gamma_i} \ul{v} \cdot f^i(d(\ul{u})) \ul{n^i}
= 0 \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl} + \delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
Notes
-----
Even though the material is linear elastic and small deformations are used, the
problem is highly nonlinear due to contacts with the planes.
Checking the tangent matrix by finite differences by setting 'check' in 'nls'
solver configuration to nonzero is rather tricky - the active contact points
must not change during the test. This can be ensured by a sufficient initial
penetration and large enough contact boundary polygons (hard!), or by tweaking
the dw_contact_plane term to mask points only by undeformed coordinates.
"""
from sfepy import data_dir
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_lame
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/cube_medium_hexa.mesh'
k = 1e5 # Elastic plane stiffness for positive penetration.
f0 = 1e2 # Force at zero penetration.
dn = 0.2 # x or y component magnitude of normals.
ds = 0.25 # Boundary polygon size in horizontal directions.
az = 0.4 # Anchor z coordinate.
options = {
'ts' : 'ts',
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'lsd',
'output_format': 'vtk',
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 3, 'Omega', 1),
}
materials = {
'solid' : ({
'D': stiffness_from_lame(dim=3, lam=5.769, mu=3.846),
},),
'cp0' : ({
'f' : [k, f0],
'.n' : [dn, 0.0, 1.0],
'.a' : [0.0, 0.0, az],
'.bs' : [[0.0, 0.0, az],
[-ds, -ds, az],
[-ds, ds, az]],
},),
'cp1' : ({
'f' : [k, f0],
'.n' : [-dn, 0.0, 1.0],
'.a' : [0.0, 0.0, az],
'.bs' : [[0.0, 0.0, az],
[ds, -ds, az],
[ds, ds, az]],
},),
'cp2' : ({
'f' : [k, f0],
'.n' : [0.0, dn, 1.0],
'.a' : [0.0, 0.0, az],
'.bs' : [[0.0, 0.0, az],
[-ds, -ds, az],
[ds, -ds, az]],
},),
'cp3' : ({
'f' : [k, f0],
'.n' : [0.0, -dn, 1.0],
'.a' : [0.0, 0.0, az],
'.bs' : [[0.0, 0.0, az],
[-ds, ds, az],
[ds, ds, az]],
},),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Bottom' : ('vertices in (z < -0.499)', 'facet'),
'Top' : ('vertices in (z > 0.499)', 'facet'),
}
ebcs = {
'fixed' : ('Bottom', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
}
equations = {
'elasticity' :
"""dw_lin_elastic.2.Omega(solid.D, v, u)
+ dw_contact_plane.2.Top(cp0.f, cp0.n, cp0.a, cp0.bs, v, u)
+ dw_contact_plane.2.Top(cp1.f, cp1.n, cp1.a, cp1.bs, v, u)
+ dw_contact_plane.2.Top(cp2.f, cp2.n, cp2.a, cp2.bs, v, u)
+ dw_contact_plane.2.Top(cp3.f, cp3.n, cp3.a, cp3.bs, v, u)
= 0""",
}
solvers = {
'lsd' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'lsi' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : 'cg',
'eps_r' : 1e-8,
'i_max' : 3000,
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 10,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'check' : 0,
'delta' : 1e-6,
}),
}
def main():
import os
from itertools import product
import numpy as nm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sfepy.discrete.fem import MeshIO
import sfepy.linalg as la
from sfepy.mechanics.contact_bodies import (ContactPlane, plot_polygon,
plot_points)
conf_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
io = MeshIO.any_from_filename(filename_mesh, prefix_dir=conf_dir)
bb = io.read_bounding_box()
outline = [vv for vv in product(*bb.T)]
ax = plot_points(None, nm.array(outline), 'r*')
for name in ['cp%d' % ii for ii in range(4)]:
cpc = materials[name][0]
cp = ContactPlane(cpc['.a'], cpc['.n'], cpc['.bs'])
v1, v2 = la.get_perpendiculars(cp.normal)
ax = plot_polygon(ax, cp.bounds)
ax = plot_polygon(ax, nm.r_[cp.anchor[None, :],
cp.anchor[None, :] + cp.normal[None, :]])
ax = plot_polygon(ax, nm.r_[cp.anchor[None, :],
cp.anchor[None, :] + v1])
ax = plot_polygon(ax, nm.r_[cp.anchor[None, :],
cp.anchor[None, :] + v2])
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()