sfepy.terms.terms_membrane module¶
- class sfepy.terms.terms_membrane.TLMembraneTerm(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Mooney-Rivlin membrane with plain stress assumption.
The membrane has a uniform initial thickness
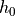 and obeys a
hyperelastic material law with strain energy by Mooney-Rivlin:
and obeys a
hyperelastic material law with strain energy by Mooney-Rivlin: 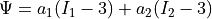 .
.- Call signature:
dw_tl_membrane
(material_a1, material_a2, material_h0, virtual, state)- Arguments:
material_a1 :
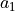
material_a2 :
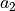
material_h0 :
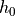
virtual :
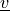
state :
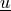
- arg_shapes = {'material_a1': '1, 1', 'material_a2': '1, 1', 'material_h0': '1, 1', 'state': 'D', 'virtual': ('D', 'state')}¶
- arg_types = ('material_a1', 'material_a2', 'material_h0', 'virtual', 'state')¶
- static function(out, fun, *args)[source]¶
Notes
fun is either weak_function or eval_function according to evaluation mode.
- geometries = ['3_4', '3_8']¶
- get_eval_shape(a1, a2, h0, virtual, state, mode=None, term_mode=None, diff_var=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
- integration = 'facet'¶
- name = 'dw_tl_membrane'¶
- sfepy.terms.terms_membrane.eval_membrane_mooney_rivlin(a1, a2, mtx_c, c33, mode)[source]¶
Evaluate stress or tangent stiffness of the Mooney-Rivlin membrane.
[1] Baoguo Wu, Xingwen Du and Huifeng Tan: A three-dimensional FE nonlinear analysis of membranes, Computers & Structures 59 (1996), no. 4, 601–605.