sfepy.solvers.nls module¶
Nonlinear solvers.
- class sfepy.solvers.nls.Newton(conf, **kwargs)[source]¶
Solves a nonlinear system
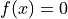 using the Newton method.
using the Newton method.The solver uses a backtracking line-search on divergence.
Kind: ‘nls.newton’
For common configuration parameters, see
Solver.Specific configuration parameters:
- Parameters:
- i_maxint (default: 1)
The maximum number of iterations.
- eps_afloat (default: 1e-10)
The absolute tolerance for the residual, i.e.
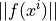 .
.- eps_rfloat (default: 1.0)
The relative tolerance for the residual, i.e.
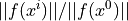 .
.- eps_mode‘and’ or ‘or’ (default: ‘and’)
The logical operator to use for combining the absolute and relative tolerances.
- machepsfloat (default: np.float64(2.220446049250313e-16))
The float considered to be machine “zero”.
- is_new_jacobian_funfunction(it, it_jac, rhs1, rhs0, x1, x0, context)
If given, the Jacobian (tangent) matrix is updated only when it returns True. it is the current iteration, it_jac the last iteration when the Jacobian was updated, rhs1, x1 are the current iteration residual, solution and rhs0, x0 are from the previous iteration. Can be used to implement the modified Newton method.
- scale_system_funfunction(mtx, rhs, x0, context)
User-defined function for scaling the linear system and initial guess in each iteration.
- scale_solution_funfunction(x, context)
User-defined function for scaling the solution in each iteration.
- scaled_errorbool (default: False)
If True, the error of the linear solver is calculated using the scaled values.
- lin_redfloat or None (default: 1.0)
The linear system solution error should be smaller than (eps_a * lin_red), otherwise a warning is printed. If None, the check is skipped.
- lin_precisionfloat or None
If not None, the linear system solution tolerances are set in each nonlinear iteration relative to the current residual norm by the lin_precision factor. Ignored for direct linear solvers.
- step_red0.0 < float <= 1.0 (default: 1.0)
Step reduction factor. Equivalent to the mixing parameter
 :
:
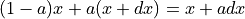
- line_search_funfunction(it, vec_x0, vec_r0, vec_dx0, err_last, conf, fun, apply_lin_solver, timers, log=None) (default: <function apply_line_search_bt at 0x73634d16caf0>)
The line search function.
- ls_mode‘residual’ or ‘error’ (default: ‘residual’)
The line search mode: when it is ‘residual’, the solver tries to make the iteration residuals decreasing while for ‘error’ the solution error estimates should decrease.
- ls_onfloat (default: 0.99999)
Start the backtracking line-search by reducing the step, if
 is larger than ls_on, where
is larger than ls_on, where 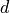 is either
is either 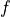 or
or 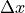 depending on ls_mode.
depending on ls_mode.- ls_red0.0 < float < 1.0 (default: 0.1)
The step reduction factor in case of correct residual assembling.
- ls_red_warp0.0 < float < 1.0 (default: 0.001)
The step reduction factor in case of failed residual assembling (e.g. the “warp violation” error caused by a negative volume element resulting from too large deformations).
- ls_min0.0 < float < 1.0 (default: 1e-05)
The minimum step reduction factor.
- give_up_warpbool (default: False)
If True, abort on the “warp violation” error.
- check0, 1 or 2 (default: 0)
If >= 1, check the tangent matrix using finite differences. If 2, plot the resulting sparsity patterns.
- deltafloat (default: 1e-06)
If check >= 1, the finite difference matrix is taken as
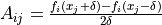 .
.- logdict or None
If not None, log the convergence according to the configuration in the following form:
{'text' : 'log.txt', 'plot' : 'log.pdf'}. Each of the dict items can be None.- log_vlines‘iteration’ or ‘solve’ or both (default: (‘solve’,))
Put log vertical lines after each iteration and/or before the solve.
- is_linearbool (default: False)
If True, the problem is considered to be linear.
- __annotations__ = {}¶
- __call__(vec_x0, conf=None, fun=None, fun_grad=None, lin_solver=None, iter_hook=None, status=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Call self as a function.
- __module__ = 'sfepy.solvers.nls'¶
- name = 'nls.newton'¶
- class sfepy.solvers.nls.PETScNonlinearSolver(conf, pmtx=None, prhs=None, comm=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Interface to PETSc SNES (Scalable Nonlinear Equations Solvers).
The solver supports parallel use with a given MPI communicator (see comm argument of
PETScNonlinearSolver.__init__()). Returns a (global) PETSc solution vector instead of a (local) numpy array, when given a PETSc initial guess vector.For parallel use, the fun and fun_grad callbacks should be provided by
PETScParallelEvaluator.Kind: ‘nls.petsc’
For common configuration parameters, see
Solver.Specific configuration parameters:
- Parameters:
- methodstr (default: ‘newtonls’)
The SNES type.
- i_maxint (default: 10)
The maximum number of iterations.
- if_maxint (default: 100)
The maximum number of function evaluations.
- eps_afloat (default: 1e-10)
The absolute tolerance for the residual, i.e.
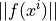 .
.- eps_rfloat (default: 1.0)
The relative tolerance for the residual, i.e.
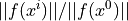 .
.- eps_sfloat (default: 0.0)
The convergence tolerance in terms of the norm of the change in the solution between steps, i.e. $||delta x|| < epsilon_s ||x||$
- __annotations__ = {}¶
- __call__(vec_x0, conf=None, fun=None, fun_grad=None, lin_solver=None, iter_hook=None, status=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Call self as a function.
- __module__ = 'sfepy.solvers.nls'¶
- name = 'nls.petsc'¶
- class sfepy.solvers.nls.ScipyRoot(conf, **kwargs)[source]¶
Interface to
scipy.optimize.root().Kind: ‘nls.scipy_root’
For common configuration parameters, see
Solver.Specific configuration parameters:
- Parameters:
- methodstr (default: ‘anderson’)
Type of solver supported in
scipy.optimize.root(), one of: [‘hybr’, ‘lm’, ‘broyden1’, ‘broyden2’, ‘anderson’, ‘linearmixing’, ‘diagbroyden’, ‘excitingmixing’, ‘krylov’, ‘df-sane’]- use_jacobianbool (default: False)
If True, use the exact Jacobian.
- tolfloat
Tolerance for termination. For detailed control, use solver-specific options.
- callbackcallback(x, f)
Optional callback function. It is called on every iteration as with x the current solution and f the corresponding residual. For all methods but ‘hybr’ and ‘lm’.
- optionsdict
A dictionary of solver options. E.g., xtol or maxiter, see
scipy.optimize.show_options('root')for details.
- __annotations__ = {}¶
- __call__(vec_x0, conf=None, fun=None, fun_grad=None, lin_solver=None, iter_hook=None, status=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Call self as a function.
- __module__ = 'sfepy.solvers.nls'¶
- methods = ['hybr', 'lm', 'broyden1', 'broyden2', 'anderson', 'linearmixing', 'diagbroyden', 'excitingmixing', 'krylov', 'df-sane']¶
- name = 'nls.scipy_root'¶
- sfepy.solvers.nls.apply_line_search_ainc(vec_x0, vec_r0, vec_dx0, it, err_last, conf, fun, apply_lin_solver, timers, log=None, context=None)[source]¶
Apply an initial step size given by Affine-Invariant Cubic Newton [1], then continue with
apply_line_search_bt().[1]S. Hanzely, D. Kamzolov, D. Pasechnyuk, A. Gasnikov, P. Richtarik, and M. Takac, A Damped Newton Method Achieves Global
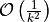 and Local Quadratic Convergence Rate,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35, 25320 (2022).
and Local Quadratic Convergence Rate,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35, 25320 (2022).
- sfepy.solvers.nls.apply_line_search_bt(vec_x0, vec_r0, vec_dx0, it, err_last, conf, fun, apply_lin_solver, timers, log=None, context=None)[source]¶
Apply a backtracking line-search on iteration residuals or error estimates depending on conf.ls_mode parameter. The error mode corresponds to the damped Newton method [1].
[1]P. Deuflhard, A modified Newton method for the solution of ill-conditioned systems of nonlinear equations with application to multiple shooting, Numer. Math. 22, 289 (1974).
- sfepy.solvers.nls.apply_line_search_ipc(vec_x0, vec_r0, vec_dx0, it, err_last, conf, fun, apply_lin_solver, timers, log=None, context=None, clog=None)[source]¶
Apply a backtracking line-search with continuous collision detection from IPC toolkit.
- sfepy.solvers.nls.check_tangent_matrix(conf, vec_x0, fun, fun_grad)[source]¶
Verify the correctness of the tangent matrix as computed by fun_grad() by comparing it with its finite difference approximation evaluated by repeatedly calling fun() with vec_x0 items perturbed by a small delta.
- sfepy.solvers.nls.conv_test(conf, it, err, err0)[source]¶
Nonlinear solver convergence test.
- Parameters:
- confStruct instance
The nonlinear solver configuration.
- itint
The current iteration.
- errfloat
The current iteration error.
- err0float
The initial error.
- Returns:
- statusint
The convergence status: -1 = no convergence (yet), 0 = solver converged - tolerances were met, 1 = max. number of iterations reached.