multi_physics/biot_short_syntax.py¶
Description
Biot problem - deformable porous medium with a no-penetration boundary condition imposed in the weak sense on a boundary region, using the short syntax of keywords.
The Biot coefficient tensor 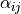 is non-symmetric. The mesh
resolution can be changed by editing the shape variable.
is non-symmetric. The mesh
resolution can be changed by editing the shape variable.
This example demonstrates how to set up various linear solvers and preconditioners (see solvers dict):
‘direct’ (a direct solver from SciPy), ‘iterative-s’ (an iterative solver from SciPy), ‘iterative-p’ (an iterative solver from PETSc) solvers can be used as the main linear solver.
‘direct’, ‘cg-s’ (several iterations of CG from SciPy), ‘cg-p’ (several iterations of CG from PETSc), ‘pyamg’ (an algebraic multigrid solver) solvers can be used as preconditioners for the matrix blocks on the diagonal.
See setup_precond() and try to modify it.
The PETSc solvers can be configured also using command line options. For
example, set 'ls' : 'iterative-p' in options, and run:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/multi_physics/biot_short_syntax.py -ksp_monitor
or simply run:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/multi_physics/biot_short_syntax.py -O "ls='iterative-p'"
to monitor the PETSc iterative solver convergence. It will diverge without
preconditioning, see matvec_bj(), matvec_j() for further
details.
The PETSc options can also be set in the solver configuration - try
uncommenting the 'ksp_*' or 'pc_*' parameters in 'iterative-p'.
Uncommenting all the lines leads to, among other things, using the GMRES method
with no preconditioning and the condition number estimate computation. Compare
the condition number estimates with and without a preconditioning (try, for
example, using 'precond' : 'mg' or 'pc_type' : 'mg').
Find 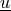 ,
, 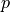 such that:
such that:
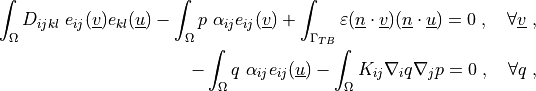
where
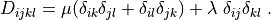
r"""
Biot problem - deformable porous medium with a no-penetration boundary
condition imposed in the weak sense on a boundary region, using the short
syntax of keywords.
The Biot coefficient tensor :math:`\alpha_{ij}` is non-symmetric. The mesh
resolution can be changed by editing the `shape` variable.
This example demonstrates how to set up various linear solvers and
preconditioners (see `solvers` dict):
- `'direct'` (a direct solver from SciPy), `'iterative-s'` (an iterative solver
from SciPy), `'iterative-p'` (an iterative solver from PETSc) solvers can be
used as the main linear solver.
- `'direct'`, `'cg-s'` (several iterations of CG from SciPy), `'cg-p'` (several
iterations of CG from PETSc), `'pyamg'` (an algebraic multigrid solver)
solvers can be used as preconditioners for the matrix blocks on the diagonal.
See :func:`setup_precond()` and try to modify it.
The PETSc solvers can be configured also using command line options. For
example, set ``'ls' : 'iterative-p'`` in `options`, and run::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/multi_physics/biot_short_syntax.py -ksp_monitor
or simply run::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/multi_physics/biot_short_syntax.py -O "ls='iterative-p'"
to monitor the PETSc iterative solver convergence. It will diverge without
preconditioning, see :func:`matvec_bj()`, :func:`matvec_j()` for further
details.
The PETSc options can also be set in the solver configuration - try
uncommenting the ``'ksp_*'`` or ``'pc_*'`` parameters in ``'iterative-p'``.
Uncommenting all the lines leads to, among other things, using the GMRES method
with no preconditioning and the condition number estimate computation. Compare
the condition number estimates with and without a preconditioning (try, for
example, using ``'precond' : 'mg'`` or ``'pc_type' : 'mg'``).
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \alpha_{ij} e_{ij}(\ul{v})
+ \int_{\Gamma_{TB}} \varepsilon (\ul{n} \cdot \ul{v}) (\ul{n} \cdot \ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
- \int_{\Omega} q\ \alpha_{ij} e_{ij}(\ul{u})
- \int_{\Omega} K_{ij} \nabla_i q \nabla_j p
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
"""
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import Struct
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_lame
from sfepy.discrete.fem.meshio import UserMeshIO
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
def get_pars(ts, coor, mode, **kwargs):
"""
Define the material parameters.
"""
if mode == 'qp':
n_nod, dim = coor.shape
out = {}
out['D'] = stiffness_from_lame(dim, lam=1.7, mu=0.3)[None, ...]
out['alpha'] = nm.array([[[0.132, 0.092],
[0.052, 0.132]]])
out['K'] = nm.eye(dim, dtype=nm.float64)[None, ...]
out['np_eps'] = nm.array([[[1e5]]])
return out
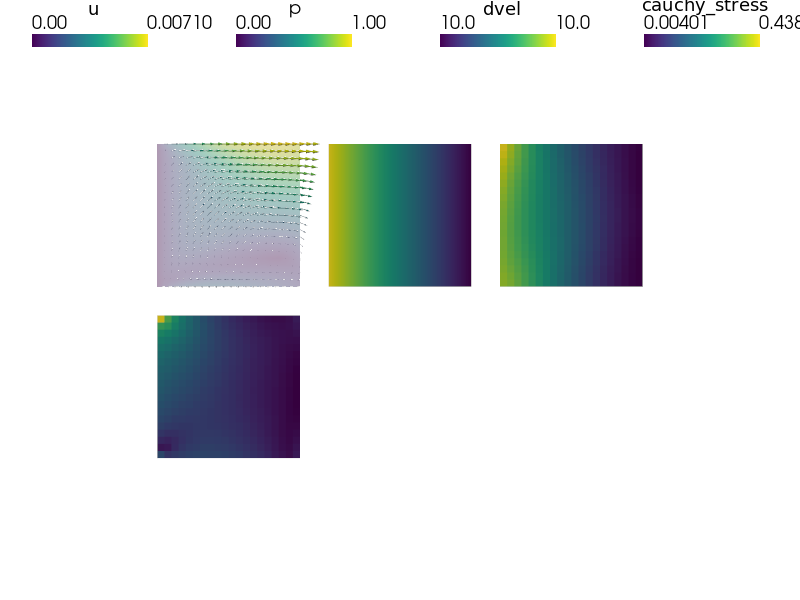
def post_process(out, pb, state, extend=False):
"""
Compute derived quantities of interest..
"""
from sfepy.base.base import Struct
dvel = pb.evaluate('ev_diffusion_velocity.i.Omega(m.K, p)',
mode='el_avg')
out['dvel'] = Struct(name='output_data',
mode='cell', data=dvel, dofs=None)
stress = pb.evaluate('ev_cauchy_stress.i.Omega(m.D, u)',
mode='el_avg')
out['cauchy_stress'] = Struct(name='output_data',
mode='cell', data=stress, dofs=None)
return out
# Mesh dimensions.
dims = [0.1, 0.1]
# Mesh resolution: increase to improve accuracy.
shape = [21, 21]
def mesh_hook(mesh, mode):
"""
Generate the block mesh.
"""
if mode == 'read':
mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, [0, 0], name='user_block',
verbose=False)
return mesh
elif mode == 'write':
pass
filename_mesh = UserMeshIO(mesh_hook)
materials = {
'coef' : ({'val' : 1.0},),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all', # or 'cells of group 6'
'GammaL' : ('vertices in (x < -0.0499)', 'facet'),
'GammaR' : ('vertices in (x > 0.0499)', 'facet'),
'GammaTB' : ('vertices of surface -s (r.GammaL +s r.GammaR)', 'facet')
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
'pressure': ('real', 'scalar', 'Omega', 1),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure', 1),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
ebcs = {
'inlet' : ('GammaL', {'p.0' : 1.0, 'u.all' : 0.0}),
'outlet' : ('GammaR', {'p.0' : 0.0}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2,
}
materials = {
'm' : 'get_pars',
}
functions = {
'get_pars' : (get_pars,),
}
equations = {
'eq_1' :
"""+ dw_lin_elastic.i.Omega(m.D, v, u)
- dw_biot.i.Omega(m.alpha, v, p)
+ dw_non_penetration_p.i.GammaTB(m.np_eps, v, u)
= 0""",
'eq_2' :
"""- dw_biot.i.Omega(m.alpha, u, q)
- dw_diffusion.i.Omega(m.K, q, p)
= 0""",
}
def setup_precond(mtx, problem):
"""
Setup a preconditioner for `mtx`.
"""
import scipy.sparse.linalg as spla
from sfepy.solvers import Solver
# Get active DOF indices for u, p.
adi = problem.get_variables().adi
iu = adi.indx['u']
ip = adi.indx['p']
# Get the diagonal blocks of the linear system matrix.
K = mtx[iu, iu]
M = mtx[ip, ip]
# Create solvers for K, M blocks to be used in matvec_bj(). A different
# solver for each block could be used.
conf = problem.solver_confs['direct']
# conf = problem.solver_confs['cg-s']
# conf = problem.solver_confs['cg-p']
# conf = problem.solver_confs['pyamg']
ls1 = Solver.any_from_conf(conf, mtx=K, context=problem)
ls2 = Solver.any_from_conf(conf, mtx=M, context=problem)
def matvec_bj(vec):
"""
The application of the Block Jacobi preconditioner.
The exact version (as with the `'direct'` solver) can be obtained also
by using the following PETSs command-line options, together with the
`'iterative-p'` solver::
-ksp_monitor -pc_type fieldsplit -pc_fieldsplit_type additive -fieldsplit_u_ksp_type preonly -fieldsplit_u_pc_type lu -fieldsplit_p_ksp_type preonly -fieldsplit_p_pc_type lu
The inexact version (20 iterations of a CG solver for each block, as
with the `'cg-s'` or `'cg-p'` solvers) can be obtained also by using
the following PETSs command-line options, together with the
`'iterative-p'` solver::
-ksp_monitor -pc_type fieldsplit -pc_fieldsplit_type additive -fieldsplit_u_ksp_type cg -fieldsplit_u_pc_type none -fieldsplit_p_ksp_type cg -fieldsplit_p_pc_type none -fieldsplit_u_ksp_max_it 20 -fieldsplit_p_ksp_max_it 20
"""
vu = ls1(vec[iu])
vp = ls2(vec[ip])
return nm.r_[vu, vp]
def matvec_j(vec):
"""
The application of the Jacobi (diagonal) preconditioner.
The same effect can be obtained also by using the following PETSs
command-line options, together with the `'iterative-p'` solver::
-ksp_monitor -pc_type jacobi
"""
D = mtx.diagonal()
return vec / D
# Create the preconditioner, using one of matvec_bj() or matvec_j().
precond = Struct(name='precond', shape=mtx.shape, matvec=matvec_bj)
precond = spla.aslinearoperator(precond)
return precond
method = 'gmres'
i_max = 20
eps_r = 1e-8
solvers = {
'direct' : ('ls.scipy_direct', {}),
'iterative-s' : ('ls.scipy_iterative', {
'method' : method,
'i_max' : i_max,
'eps_r' : eps_r,
'setup_precond': setup_precond,
'verbose' : 2,
}),
'cg-s' : ('ls.scipy_iterative', {
'method' : 'cg',
'i_max' : 20,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
'verbose' : 0,
}),
'iterative-p' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : method,
'precond' : 'none',
'i_max' : i_max,
'eps_r' : eps_r,
'verbose' : 2,
# 'ksp_converged_reason' : None,
# 'ksp_monitor_true_residual' : None,
# 'ksp_monitor_singular_value' : None,
# 'ksp_final_residual' : None,
# 'ksp_type' : 'gmres', # Overrides `method`.
# 'ksp_max_it' : 500,
# 'ksp_gmres_restart' : 1000,
# 'pc_type' : 'none', # Overrides `precond`.
}),
'cg-p' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : 'cg',
'precond' : 'none',
'i_max' : 20,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
'verbose' : 0,
}),
'pyamg' : ('ls.pyamg', {
'method' : 'smoothed_aggregation_solver',
'i_max' : 20,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
'verbose' : 0,
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton',
{'i_max' : 1,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
'eps_a' : 1.0,
}),
}
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'iterative-s',
'post_process_hook' : 'post_process',
}