linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py¶
Description
Bending of a long thin cantilever beam, imperative problem description.
The example demonstrates use of the
dw_shell10x term.
Find displacements of the central plane 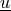 , and rotations
, and rotations
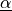 such that:
such that:
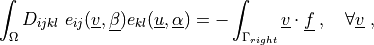
where 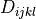 is the isotropic elastic tensor, given using the Young’s
modulus
is the isotropic elastic tensor, given using the Young’s
modulus 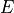 and the Poisson’s ratio
and the Poisson’s ratio 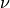 .
.
The variable u below holds both 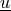 and
and 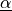 DOFs. For visualization, it is saved as two fields
DOFs. For visualization, it is saved as two fields u_disp and u_rot,
corresponding to 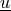 and
and 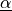 , respectively.
, respectively.
The material, loading and discretization parameters can be given using command line options.
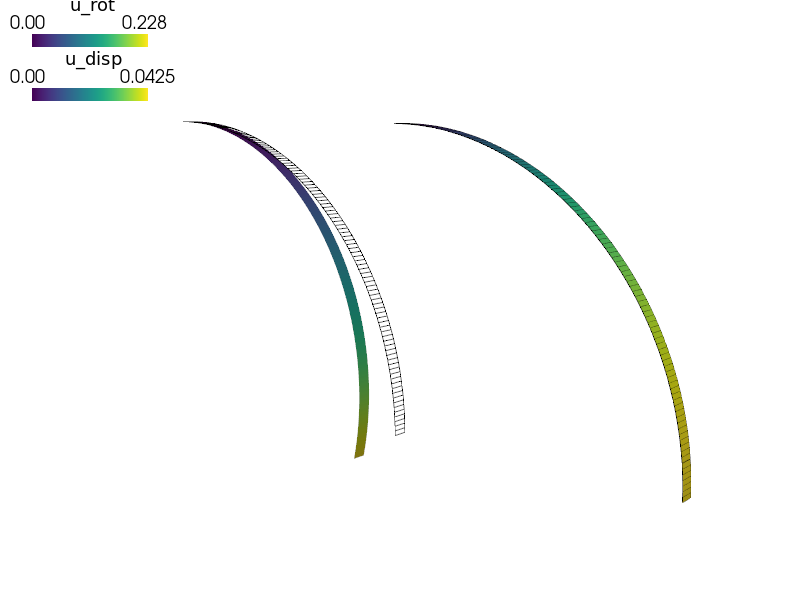
Besides the default straight beam, two coordinate transformations can be applied
(see the --transform option):
bend: the beam is bent
twist: the beam is twisted
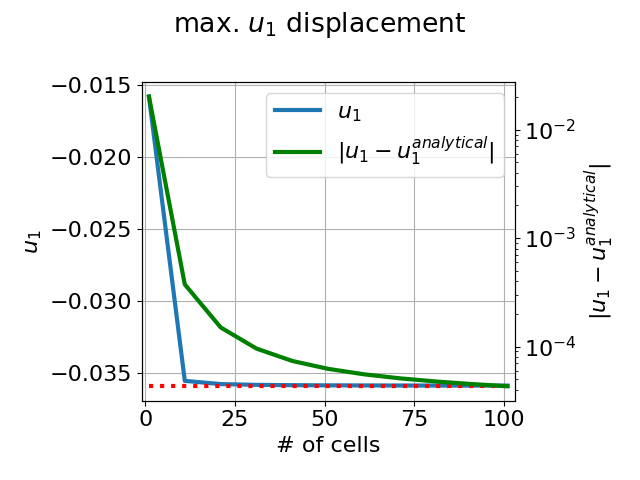
For the straight and bent beam a comparison with the analytical solution coming from the Euler-Bernoulli theory is shown.
See also linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever.py example.
Usage Examples¶
See all options:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py -h
Apply the bending transformation to the beam domain coordinates, plot convergence curves w.r.t. number of elements:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py output -t bend -p
Apply the twisting transformation to the beam domain coordinates, change number of cells:
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py output -t twist -n 2,51,3
#!/usr/bin/env python
r"""
Bending of a long thin cantilever beam, imperative problem description.
The example demonstrates use of the
:class:`dw_shell10x <sfepy.terms.terms_shells.Shell10XTerm>` term.
Find displacements of the central plane :math:`\ul{u}`, and rotations
:math:`\ul{\alpha}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}, \ul{\beta})
e_{kl}(\ul{u}, \ul{\alpha})
= - \int_{\Gamma_{right}} \ul{v} \cdot \ul{f}
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
where :math:`D_{ijkl}` is the isotropic elastic tensor, given using the Young's
modulus :math:`E` and the Poisson's ratio :math:`\nu`.
The variable ``u`` below holds both :math:`\ul{u}` and :math:`\ul{\alpha}`
DOFs. For visualization, it is saved as two fields ``u_disp`` and ``u_rot``,
corresponding to :math:`\ul{u}` and :math:`\ul{\alpha}`, respectively.
The material, loading and discretization parameters can be given using command
line options.
Besides the default straight beam, two coordinate transformations can be applied
(see the ``--transform`` option):
- bend: the beam is bent
- twist: the beam is twisted
For the straight and bent beam a comparison with the analytical solution
coming from the Euler-Bernoulli theory is shown.
See also :ref:`linear_elasticity-shell10x_cantilever` example.
Usage Examples
--------------
See all options::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py -h
Apply the bending transformation to the beam domain coordinates, plot
convergence curves w.r.t. number of elements::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py output -t bend -p
Apply the twisting transformation to the beam domain coordinates, change number of cells::
python3 sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/shell10x_cantilever_interactive.py output -t twist -n 2,51,3
"""
from argparse import RawDescriptionHelpFormatter, ArgumentParser
import os
import sys
sys.path.append('.')
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import output, IndexedStruct
from sfepy.base.ioutils import ensure_path
from sfepy.discrete import (FieldVariable, Material, Integral,
Equation, Equations, Problem)
from sfepy.discrete.fem import Mesh, FEDomain, Field
from sfepy.terms import Term
from sfepy.discrete.conditions import Conditions, EssentialBC
from sfepy.solvers.auto_fallback import AutoDirect
from sfepy.solvers.nls import Newton
from sfepy.linalg import make_axis_rotation_matrix
from sfepy.mechanics.tensors import transform_data
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
import sfepy.mechanics.shell10x as sh
def make_mesh(dims, shape, transform=None):
"""
Generate a 2D rectangle mesh in 3D space, and optionally apply a coordinate
transform.
"""
_mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, [0, 0], name='shell10x', verbose=False)
coors = nm.c_[_mesh.coors, nm.zeros(_mesh.n_nod, dtype=nm.float64)]
coors = nm.ascontiguousarray(coors)
conns = [_mesh.get_conn(_mesh.descs[0])]
mesh = Mesh.from_data(_mesh.name, coors, _mesh.cmesh.vertex_groups, conns,
[_mesh.cmesh.cell_groups], _mesh.descs)
if transform == 'bend':
bbox = mesh.get_bounding_box()
x0, x1 = bbox[:, 0]
angles = 0.5 * nm.pi * (coors[:, 0] - x0) / (x1 - x0)
mtx = make_axis_rotation_matrix([0, -1, 0], angles[:, None, None])
coors = mesh.coors.copy()
coors[:, 0] = 0
coors[:, 2] = (x1 - x0)
mesh.coors[:] = transform_data(coors, mtx=mtx)
mesh.coors[:, 0] -= 0.5 * (x1 - x0)
elif transform == 'twist':
bbox = mesh.get_bounding_box()
x0, x1 = bbox[:, 0]
angles = 0.5 * nm.pi * (coors[:, 0] - x0) / (x1 - x0)
mtx = make_axis_rotation_matrix([-1, 0, 0], angles[:, None, None])
mesh.coors[:] = transform_data(mesh.coors, mtx=mtx)
return mesh
def make_domain(dims, shape, transform=None):
"""
Generate a 2D rectangle domain in 3D space, define regions.
"""
xmin = (-0.5 + 1e-12) * dims[0]
xmax = (0.5 - 1e-12) * dims[0]
mesh = make_mesh(dims, shape, transform=transform)
domain = FEDomain('domain', mesh)
domain.create_region('Omega', 'all')
domain.create_region('Gamma1', 'vertices in (x < %.14f)' % xmin, 'facet')
domain.create_region('Gamma2', 'vertices in (x > %.14f)' % xmax, 'facet')
return domain
def solve_problem(shape, dims, young, poisson, force, transform=None):
domain = make_domain(dims[:2], shape, transform=transform)
omega = domain.regions['Omega']
gamma1 = domain.regions['Gamma1']
gamma2 = domain.regions['Gamma2']
field = Field.from_args('fu', nm.float64, 6, omega, approx_order=1,
poly_space_basis='shell10x')
u = FieldVariable('u', 'unknown', field)
v = FieldVariable('v', 'test', field, primary_var_name='u')
thickness = dims[2]
if transform is None:
pload = [[0.0, 0.0, force / shape[1], 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]] * shape[1]
elif transform == 'bend':
pload = [[force / shape[1], 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]] * shape[1]
elif transform == 'twist':
pload = [[0.0, force / shape[1], 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]] * shape[1]
m = Material('m', D=sh.create_elastic_tensor(young=young, poisson=poisson),
values={'.drill' : 1e-7})
load = Material('load', values={'.val' : pload})
aux = Integral('i', order=3)
qp_coors, qp_weights = aux.get_qp('3_8')
qp_coors[:, 2] = thickness * (qp_coors[:, 2] - 0.5)
qp_weights *= thickness
integral = Integral('i', coors=qp_coors, weights=qp_weights, order='custom')
t1 = Term.new('dw_shell10x(m.D, m.drill, v, u)',
integral, omega, m=m, v=v, u=u)
t2 = Term.new('dw_point_load(load.val, v)',
integral, gamma2, load=load, v=v)
eq = Equation('balance', t1 - t2)
eqs = Equations([eq])
fix_u = EssentialBC('fix_u', gamma1, {'u.all' : 0.0})
ls = AutoDirect({})
nls_status = IndexedStruct()
nls = Newton({}, lin_solver=ls, status=nls_status)
pb = Problem('elasticity with shell10x', equations=eqs)
pb.set_bcs(ebcs=Conditions([fix_u]))
pb.set_solver(nls)
state = pb.solve()
return pb, state, u, gamma2
def get_analytical_displacement(dims, young, force, transform=None):
"""
Returns the analytical value of the max. displacement according to
Euler-Bernoulli theory.
"""
l, b, h = dims
if transform is None:
moment = b * h**3 / 12.0
u = force * l**3 / (3 * young * moment)
elif transform == 'bend':
u = force * 3.0 * nm.pi * l**3 / (young * b * h**3)
elif transform == 'twist':
u = None
return u
helps = {
'output_dir' : 'output directory',
'dims' :
'dimensions of the cantilever [default: %(default)s]',
'nx' :
'the range for the numbers of cells in the x direction'
' [default: %(default)s]',
'transform' :
'the transformation of the domain coordinates [default: %(default)s]',
'young' : "the Young's modulus [default: %(default)s]",
'poisson' : "the Poisson's ratio [default: %(default)s]",
'force' : "the force load [default: %(default)s]",
'plot' : 'plot the max. displacement w.r.t. number of cells',
'no_show' : 'do not show matplotlib figures',
'silent' : 'do not print messages to screen',
}
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(description=__doc__.rstrip(),
formatter_class=RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('output_dir', help=helps['output_dir'])
parser.add_argument('-d', '--dims', metavar='l,w,t',
action='store', dest='dims',
default='0.2,0.01,0.001', help=helps['dims'])
parser.add_argument('-n', '--nx', metavar='start,stop,step',
action='store', dest='nx',
default='2,103,10', help=helps['nx'])
parser.add_argument('-t', '--transform', choices=['none', 'bend', 'twist'],
action='store', dest='transform',
default='none', help=helps['transform'])
parser.add_argument('--young', metavar='float', type=float,
action='store', dest='young',
default=210e9, help=helps['young'])
parser.add_argument('--poisson', metavar='float', type=float,
action='store', dest='poisson',
default=0.3, help=helps['poisson'])
parser.add_argument('--force', metavar='float', type=float,
action='store', dest='force',
default=-1.0, help=helps['force'])
parser.add_argument('-p', '--plot',
action="store_true", dest='plot',
default=False, help=helps['plot'])
parser.add_argument('--no-show',
dest='show', action='store_false',
default=True, help=helps['no_show'])
parser.add_argument('--silent',
action='store_true', dest='silent',
default=False, help=helps['silent'])
options = parser.parse_args()
dims = nm.array([float(ii) for ii in options.dims.split(',')],
dtype=nm.float64)
nxs = tuple([int(ii) for ii in options.nx.split(',')])
young = options.young
poisson = options.poisson
force = options.force
output_dir = options.output_dir
odir = lambda filename: os.path.join(output_dir, filename)
filename = odir('output_log.txt')
ensure_path(filename)
output.set_output(filename=filename, combined=options.silent == False)
output('output directory:', output_dir)
output('using values:')
output(" dimensions:", dims)
output(" nx range:", nxs)
output(" Young's modulus:", options.young)
output(" Poisson's ratio:", options.poisson)
output(' force:', options.force)
output(' transform:', options.transform)
if options.transform == 'none':
options.transform = None
u_exact = get_analytical_displacement(dims, young, force,
transform=options.transform)
if options.transform is None:
ilog = 2
labels = ['u_3']
elif options.transform == 'bend':
ilog = 0
labels = ['u_1']
elif options.transform == 'twist':
ilog = [0, 1, 2]
labels = ['u_1', 'u_2', 'u_3']
label = ', '.join(labels)
log = []
for nx in range(*nxs):
shape = (nx, 2)
pb, state, u, gamma2 = solve_problem(shape, dims, young, poisson, force,
transform=options.transform)
dofs = u.get_state_in_region(gamma2)
output('DOFs along the loaded edge:')
output('\n%s' % dofs)
log.append([nx - 1] + nm.array(dofs[0, ilog], ndmin=1).tolist())
pb.save_state(odir('shell10x_cantilever.vtk'), state)
log = nm.array(log)
output('max. %s displacement w.r.t. number of cells:' % label)
output('\n%s' % log)
output('analytical value:', u_exact)
if options.plot:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({
'lines.linewidth' : 3,
'font.size' : 16,
})
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
fig.suptitle('max. $%s$ displacement' % label)
for ic in range(log.shape[1] - 1):
ax1.plot(log[:, 0], log[:, ic + 1], label=r'$%s$' % labels[ic])
ax1.set_xlabel('# of cells')
ax1.set_ylabel(r'$%s$' % label)
ax1.grid(which='both')
lines1, labels1 = ax1.get_legend_handles_labels()
if u_exact is not None:
ax1.hlines(u_exact, log[0, 0], log[-1, 0],
'r', 'dotted', label=r'$%s^{analytical}$' % label)
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
# Assume single log column.
ax2.semilogy(log[:, 0], nm.abs(log[:, 1] - u_exact), 'g',
label=r'$|%s - %s^{analytical}|$' % (label, label))
ax2.set_ylabel(r'$|%s - %s^{analytical}|$' % (label, label))
lines2, labels2 = ax2.get_legend_handles_labels()
else:
lines2, labels2 = [], []
ax1.legend(lines1 + lines2, labels1 + labels2, loc='best')
plt.tight_layout()
ax1.set_xlim([log[0, 0] - 2, log[-1, 0] + 2])
suffix = {None: 'straight',
'bend' : 'bent', 'twist' : 'twisted'}[options.transform]
fig.savefig(odir('shell10x_cantilever_convergence_%s.png' % suffix))
if options.show:
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()